Induction Brazing Basics for jointing copper,silver,brazing,steel and stainless steel,etc.
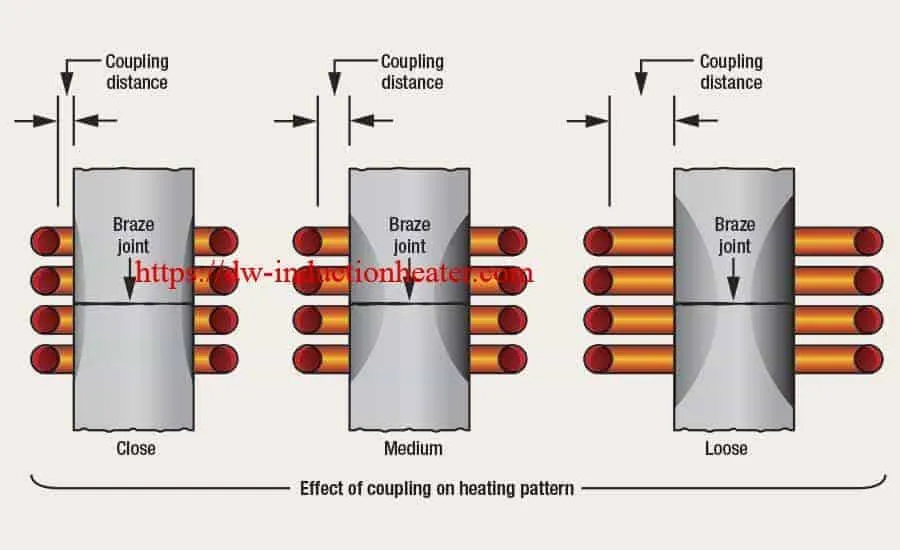
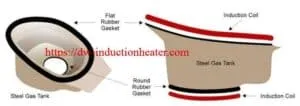
Induction Brazing uses heat and filler metal to join metals. Once melted, the filler flows between close-fitting base metals (the pieces being joined) by capillary action. The molten filler interacts with a thin layer of the base metal to form a strong, leak-proof joint. Different heat sources can be used for brazing: induction and resistance heaters, ovens, furnaces, torches, etc. There are three common brazing methods: capillary, notch and moulding. Induction brazing is concerned solely with the first of these. Having the correct gap between the base metals is crucial. A too-large gap can minimize the capillary force and lead to weak joints and porosity. Thermal expansion means gaps have to be calculated for metals at brazing, not room, temperatures. Optimum spacing is typically 0.05 mm – 0.1 mm. Before you braze Brazing is hassle-free. But some questions should be investigated — and answered — in order to assure successful, cost-effective joining. For instance: How suitable are the base metals for brazing; what’s the best coil design for specific time and quality demands; should the brazing be manual or automatic?

At DAWEI Induction we answer these and other key points before suggesting a brazing solution. Focus on flux Base metals must usually be coated with a solvent known as flux before they are brazed. Flux cleans the base metals, prevents new oxidation, and wets the brazing area prior to brazing. It is crucial to apply sufficient flux; too little and the flux may become
saturated with oxides and lose its ability to protect the base metals. Flux is not always needed. Phosphorous-bearing filler
can be used to braze copper alloys, brass and bronze. Flux-free brazing is also possible with active atmospheres and vacuums, but the brazing must then be performed in a controlled atmosphere chamber. Flux must normally be removed from the part once the metal filler has solidified. Different removal methods are used, the most common being water quenching, pickling and wire brushing.