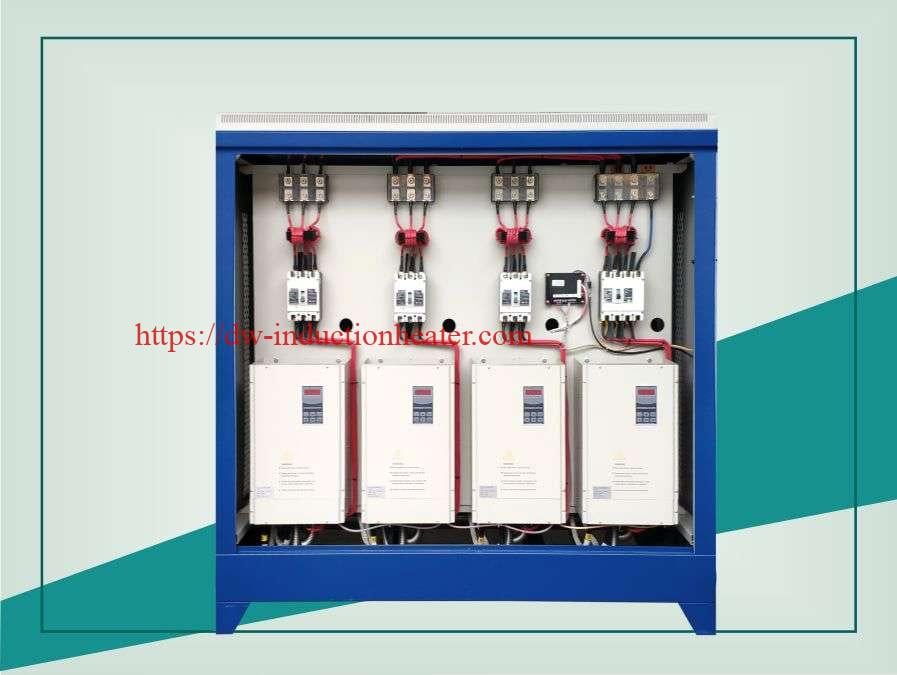
-
1/5

-
2/5

-
3/5

-
4/5

Revolutionizing Residential Heating Solutions with Induction Water Heaters
As homeowners seek more efficient, reliable, and eco-friendly ways to heat their living spaces, induction water heaters have emerged as a compelling option. Leveraging the principles of electromagnetic induction, these systems heat water quickly, deliver consistent warmth, and reduce overall energy consumption. This article explores the key benefits, applications, and considerations for using induction water heaters in residential heating solutions.
How Electromagnetic Induction Water Heating Works
Electromagnetic induction water heaters operate on Michael Faraday’s principle of electromagnetic induction. When alternating current flows through a coil (inductor), it creates a fluctuating magnetic field. This magnetic field induces eddy currents in conductive materials, generating heat through electrical resistance. In water heating applications, specially designed induction coils transfer energy directly to water passing through the system, achieving remarkable heating efficiency of up to 99%.
Key Principles
- Eddy Currents: Rapidly alternating electromagnetic fields induce currents within the metal.
- Direct Heating: Unlike traditional resistance-based systems, the heating occurs directly in the metal, maximizing energy transfer.
- Quick Response: The heat generated is immediate, allowing faster temperature adjustments compared with conventional heating methods.
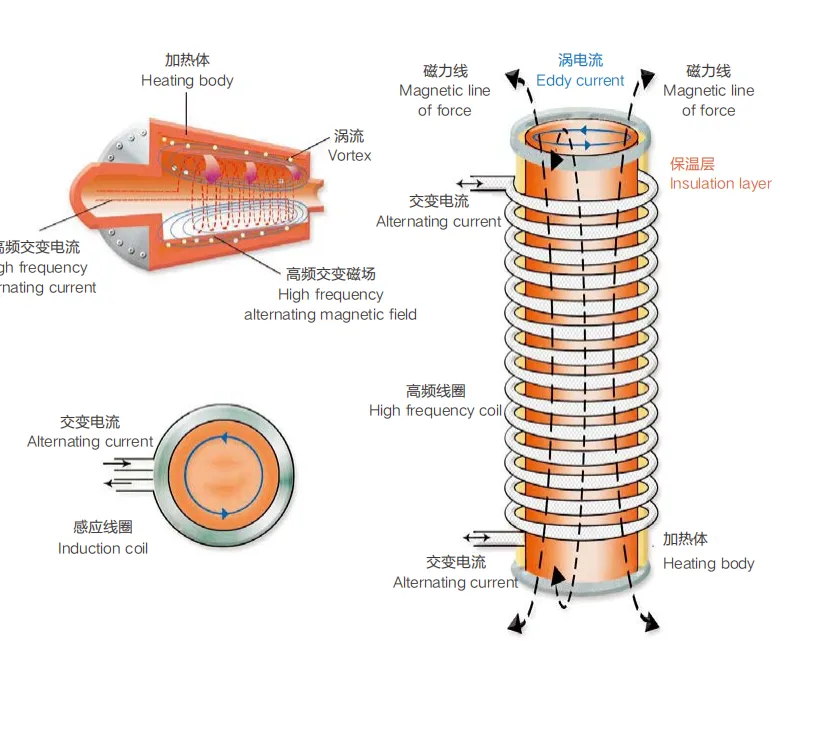
Unlike conventional heating methods that rely on heat transfer through surfaces, induction heating generates heat directly within the water, eliminating thermal losses associated with traditional systems. This direct energy conversion results in faster heating times, precise temperature control, and significantly reduced energy consumption.
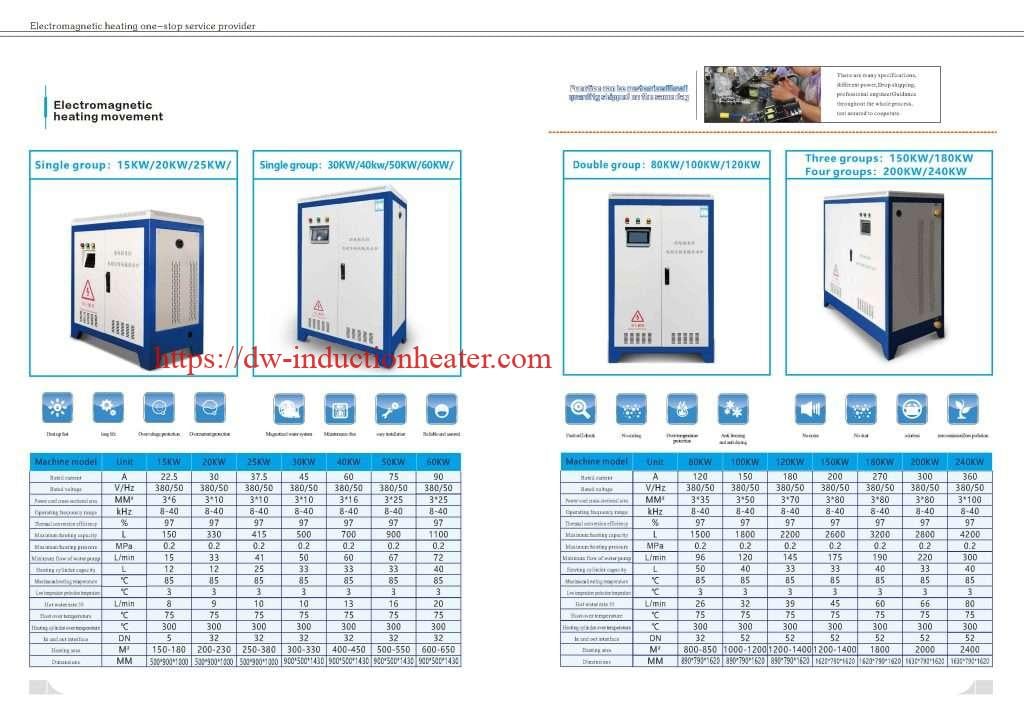
Technical Parameters and Specifications
Electromagnetic induction water heaters are available in various power capacities to suit different applications. The following tables provide detailed technical specifications across different power ranges:
Table 1: Small to Medium Capacity Induction Water Heaters (30kW-200kW)
| Parameter | 30kW Model | 60kW Model | 100kW Model | 150kW Model | 200kW Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 380V±10%, 3-phase | 380V±10%, 3-phase | 380V±10%, 3-phase | 380V±10%, 3-phase | 380V±10%, 3-phase |
| Frequency | 50/60Hz | 50/60Hz | 50/60Hz | 50/60Hz | 50/60Hz |
| Power Factor | ≥0.95 | ≥0.95 | ≥0.96 | ≥0.96 | ≥0.97 |
| Heating Efficiency | 98% | 98% | 98.5% | 99% | 99% |
| Water Flow Rate | 0.5-1.5 m³/h | 1.0-3.0 m³/h | 1.7-5.0 m³/h | 2.5-7.5 m³/h | 3.4-10.0 m³/h |
| Max Water Temp | 95°C | 95°C | 98°C | 98°C | 98°C |
| Temp Control Precision | ±1°C | ±1°C | ±0.8°C | ±0.8°C | ±0.5°C |
| Working Pressure | ≤0.6MPa | ≤0.6MPa | ≤0.8MPa | ≤0.8MPa | ≤1.0MPa |
| Cooling Method | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled |
| Protection Grade | IP54 | IP54 | IP54 | IP54 | IP54 |
Table 2: High Capacity Industrial Induction Water Heaters (250kW-800kW)
| Parameter | 250kW Model | 350kW Model | 500kW Model | 650kW Model | 800kW Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 380V±10%, 3-phase | 380V±10%, 3-phase | 380V±10%, 3-phase | 380V/480V, 3-phase | 380V/480V, 3-phase |
| Frequency | 50/60Hz | 50/60Hz | 50/60Hz | 50/60Hz | 50/60Hz |
| Power Factor | ≥0.97 | ≥0.97 | ≥0.98 | ≥0.98 | ≥0.98 |
| Heating Efficiency | 99% | 99% | 99% | 99% | 99% |
| Water Flow Rate | 4.3-12.5 m³/h | 6.0-17.5 m³/h | 8.5-25.0 m³/h | 11.0-32.5 m³/h | 13.6-40.0 m³/h |
| Max Water Temp | 98°C | 98°C | 99°C | 99°C | 99°C |
| Temp Control Precision | ±0.5°C | ±0.5°C | ±0.3°C | ±0.3°C | ±0.3°C |
| Working Pressure | ≤1.0MPa | ≤1.0MPa | ≤1.2MPa | ≤1.2MPa | ≤1.6MPa |
| Cooling Method | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled | Water-cooled |
| Protection Grade | IP54 | IP54 | IP54 | IP54 | IP54 |
| IGBT Protection | Advanced | Advanced | Advanced | Advanced | Advanced |
| Control System | PLC + HMI | PLC + HMI | PLC + HMI | PLC + HMI | PLC + HMI |
Performance Analysis and Efficiency Metrics
Energy Efficiency Analysis
Electromagnetic induction water heaters demonstrate remarkable energy efficiency advantages over conventional heating systems. The following data analysis highlights the comparative performance:
| Heating Method | Energy Efficiency | Heat-up Time (50°C rise) | Annual Energy Consumption* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Water Heater | 95-99% | 60-90 seconds | 100% (baseline) |
| Electric Resistance Heater | 70-80% | 180-240 seconds | 125-135% |
| Gas Water Heater | 55-75% | 240-300 seconds | 130-150% |
| Oil-fired Boiler | 50-70% | 300-360 seconds | 140-160% |
*For equivalent heating capacity, normalized to induction heater consumption
Temperature Rise Performance
The following graph data demonstrates the rapid temperature rise capabilities of induction water heaters across different power ratings:
| Power Rating | Temp Rise (°C/min) at 50% Flow | Temp Rise (°C/min) at 75% Flow | Temp Rise (°C/min) at 100% Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30kW | 50-55 | 35-40 | 25-30 |
| 100kW | 52-58 | 37-42 | 27-32 |
| 250kW | 55-60 | 38-43 | 28-33 |
| 500kW | 58-63 | 40-45 | 30-35 |
| 800kW | 60-65 | 42-47 | 32-37 |
Return on Investment Analysis
Based on operational data from industrial installations, electromagnetic induction water heaters demonstrate compelling ROI metrics:
| Parameter | Small Scale (30-100kW) | Medium Scale (100-350kW) | Large Scale (350-800kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment Premium* | +30-40% | +25-35% | +20-30% |
| Annual Energy Savings | 20-30% | 25-35% | 30-40% |
| Maintenance Cost Reduction | 40-50% | 45-55% | 50-60% |
| Typical Payback Period | 1.5-2.5 years | 1.2-2.0 years | 0.8-1.5 years |
| Lifetime Cost Advantage | 30-40% | 35-45% | 40-50% |
*Compared to conventional heating systems of equivalent capacity
Key Advantages of Electromagnetic Induction Water Heaters
1. Unparalleled Energy Efficiency
With efficiency ratings of up to 99%, electromagnetic induction water heaters convert virtually all electrical energy into heat, minimizing waste and reducing operational costs. The direct energy transfer mechanism eliminates intermediate heat exchanges that typically result in thermal losses.
2. Precise Temperature Control
Advanced digital control systems enable temperature precision within ±0.3°C, ensuring consistent water temperature for critical processes. This precision is particularly valuable in industrial applications where temperature stability directly impacts product quality.
3. Rapid Heating Response
Induction heating systems can reach target temperatures within seconds, eliminating warm-up periods associated with conventional systems. This responsiveness allows for on-demand heating, reducing standby energy consumption.
4. Compact Design and Space Efficiency
Modern electromagnetic induction water heaters require up to 70% less installation space compared to traditional boiler systems, offering significant advantages for facilities with limited space.
5. Environmental Benefits
Induction water heaters produce zero direct emissions, supporting carbon reduction goals. Their high efficiency translates to reduced energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions from power generation.
6. Reduced Maintenance Requirements
The absence of combustion components, heating elements, and complex mechanical systems results in minimal maintenance needs and extended operational life. Most systems require only annual inspection rather than regular component replacement.
Applications Across Industries
Electromagnetic induction water heaters are highly efficient and versatile devices that leverage the principles of electromagnetic induction to heat water. Their applications span a variety of sectors due to their efficiency, reliability, and compact design. Here are some of the key applications:
- Domestic Hot Water Supply
- Residential tankless water heaters that use electromagnetic induction for on-demand, efficient hot water with minimal heat loss.
- Central Heating and HVAC Systems
- Integration into home or commercial heating systems, providing a rapid heating source for radiators and water-based HVAC solutions.
- Commercial Kitchens and Food Service
- Rapid water heating for dishwashers, sanitizers, and other commercial appliances where quick, precise temperature control is essential.
- Laundry and Textile Facilities
- Industrial-scale induction heaters for hot water supply in laundromats and textile dyeing processes, boosting efficiency while reducing downtime.
- Industrial Process Heating
- Automotive and Car Wash Facilities
- Supplying on-demand hot water for vehicle cleaning and detailing services, taking advantage of efficient energy use and fast temperature ramp-up.
- Sterilization and Sanitation
- Hospitals, research laboratories, and veterinary clinics often require reliable high-temperature water for sterilizers, autoclaves, or cleaning systems.
- Hot Water Supply for Swimming Pools and Spas
- Using electromagnetic induction heaters in conjunction with pumps and filtration systems for faster heating and precise temperature maintenance.
- Remote or Off-Grid Locations
- Potentially paired with renewable energy sources (solar, wind) for efficient on-demand water heating in cabins, remote healthcare centers, or mobile installations.
- Heat Recovery and Circulation Systems
- Integration with heat exchangers or closed-loop systems where induction-based heating complements or replaces traditional boiler elements.
Across all these applications, the main advantages of electromagnetic induction water heaters include rapid heating speeds, high energy efficiency, improved safety (no open flame), and reduced scaling issues compared to conventional resistance heating systems.
Considerations Before Installation
Electrical Infrastructure
Induction heaters may require high-power connections, especially for larger homes or simultaneous demands (e.g., multiple showers running). Ensure that your electrical panel can handle the load and meets local code requirements. Consult a licensed electrician if upgrades are needed.
System Sizing and Load Analysis
Accurate sizing is critical—an undersized unit may not provide sufficient heating, while an oversized system could lead to energy inefficiencies and higher upfront costs. Work with a qualified heating professional to assess your home’s heating and hot water needs.
Water Quality and Hardness
Though less susceptible to limescale formation than traditional heating elements, induction systems still encounter scale deposits in areas with very hard water. Installing a water softener or filtration system can help maintain optimal performance and extend the heater’s lifespan.
Local Regulations and Rebates
Some regions provide incentives, rebates, or tax credits for homeowners investing in energy-efficient appliances. Check local utility programs or government initiatives to see if you qualify. Be sure to confirm that your chosen induction water heater meets local building codes and environmental standards.
Future Trends and Innovations
The electromagnetic induction water heating market continues to evolve with several emerging trends:
- Smart Integration: Modern systems increasingly feature IoT connectivity, allowing remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and integration with building management systems.
- Hybrid Systems: Manufacturers are developing hybrid solutions that combine induction heating with renewable energy sources like solar thermal and heat pumps.
- Advanced Materials: Research into specialized magnetic materials promises to further enhance efficiency and reduce manufacturing costs.
- Miniaturization: Compact designs are expanding applications into residential markets previously dominated by conventional water heaters.

Conclusion
Electromagnetic induction water heaters represent a significant advancement in residential heating technology. Induction water heaters represent an evolution in residential heating technologies, offering unmatched energy efficiency, eco-friendliness, and modern convenience. If you’re planning to upgrade your home’s water heating system, these compact and innovative solutions are worth the investment. Embracing induction water heaters not only enhances comfort at home but also contributes to a greener future.