-
1/6

-
2/6

-
3/6

-
4/6

-
5/6

-
6/6

rail hardening system and scanner for induction quenching solutions
The Evolution and Impact of Rail Hardening Systems and Scanners on Modern Railways
In the industrial landscape, the evolution of metallurgical processes and the adoption of advanced machining technologies have been pivotal in enhancing the operational efficacy and longevity of crucial components. Among the myriad of innovations, the development and application of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) induction rail hardening systems stand out as a cornerstone in the advancement of railway infrastructure. This essay delves into the intricacies of this technology, exploring its principles, components, benefits, challenges, and the ongoing research aimed at refining and optimizing the process.
The Principle of Induction Rail Hardening
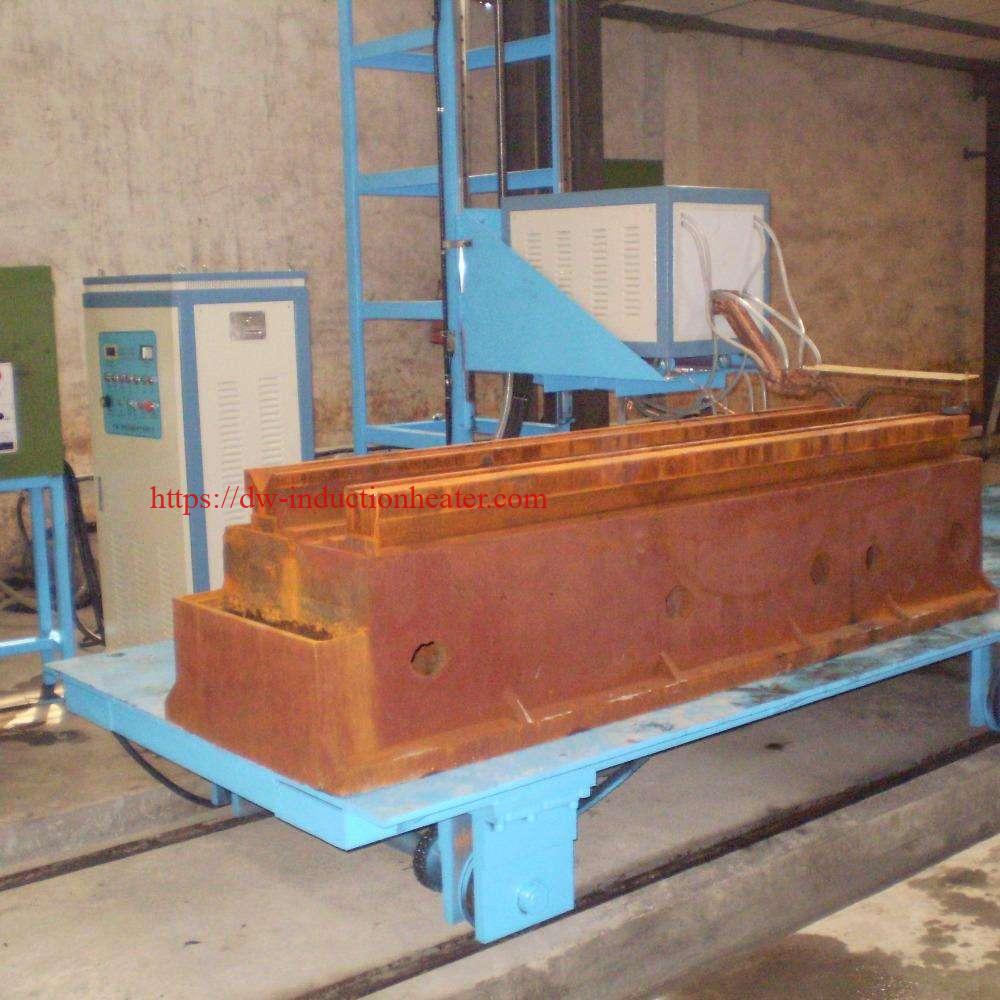
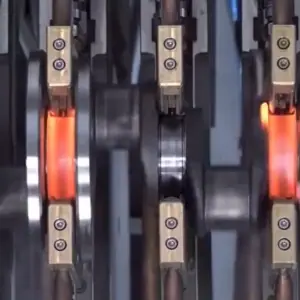
At the heart of CNC induction rail hardening technology lies the principle of electromagnetic induction, a process that has revolutionized the way steel rails are hardened. This method involves the heating of steel rails to the austenitizing temperature, followed by a rapid cooling or quenching phase. The transformation induced by this thermal cycling alters the microstructure of the steel, significantly enhancing its hardness and, consequently, its durability and wear resistance. The precise control afforded by CNC technology makes it possible to achieve consistent and optimal hardening results, tailored to the specific requirements of different rail profiles and compositions.
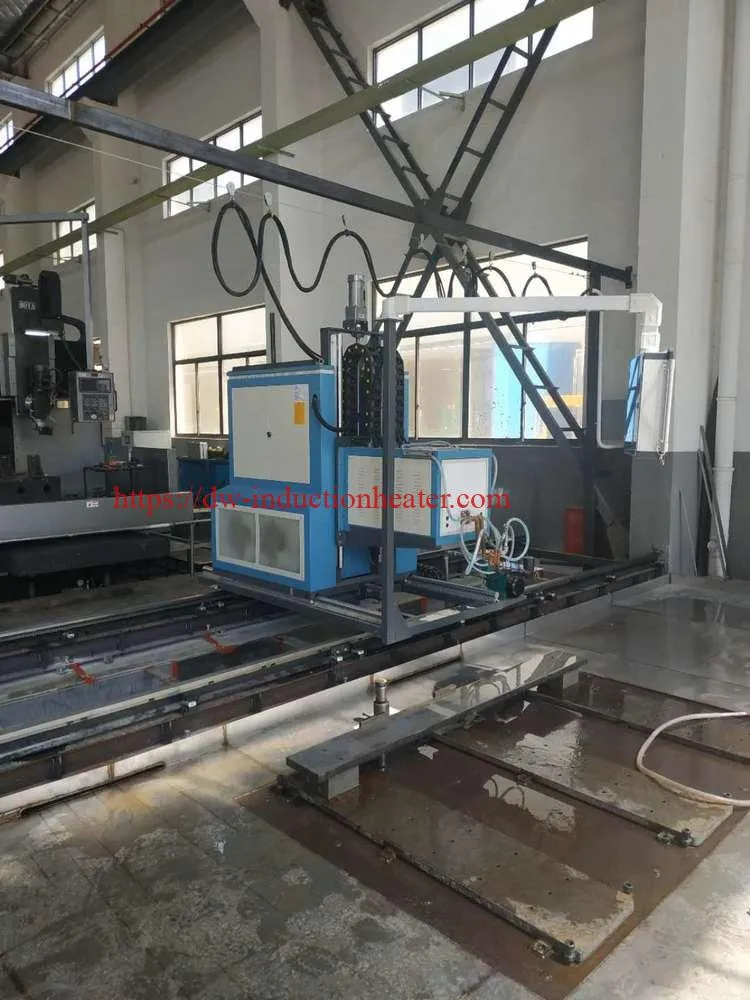
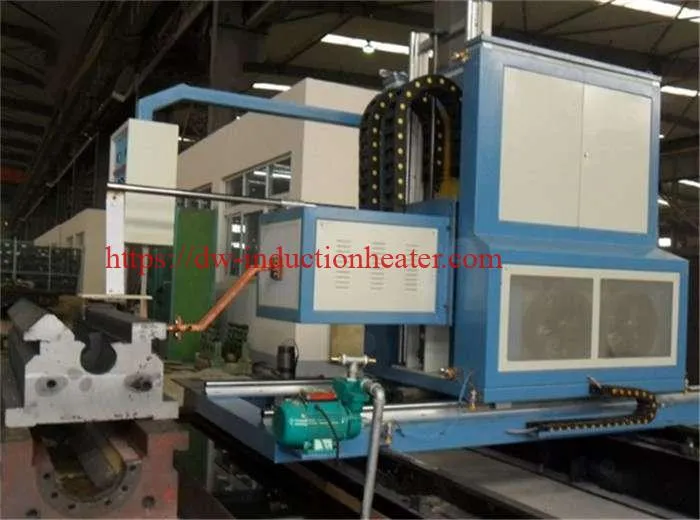
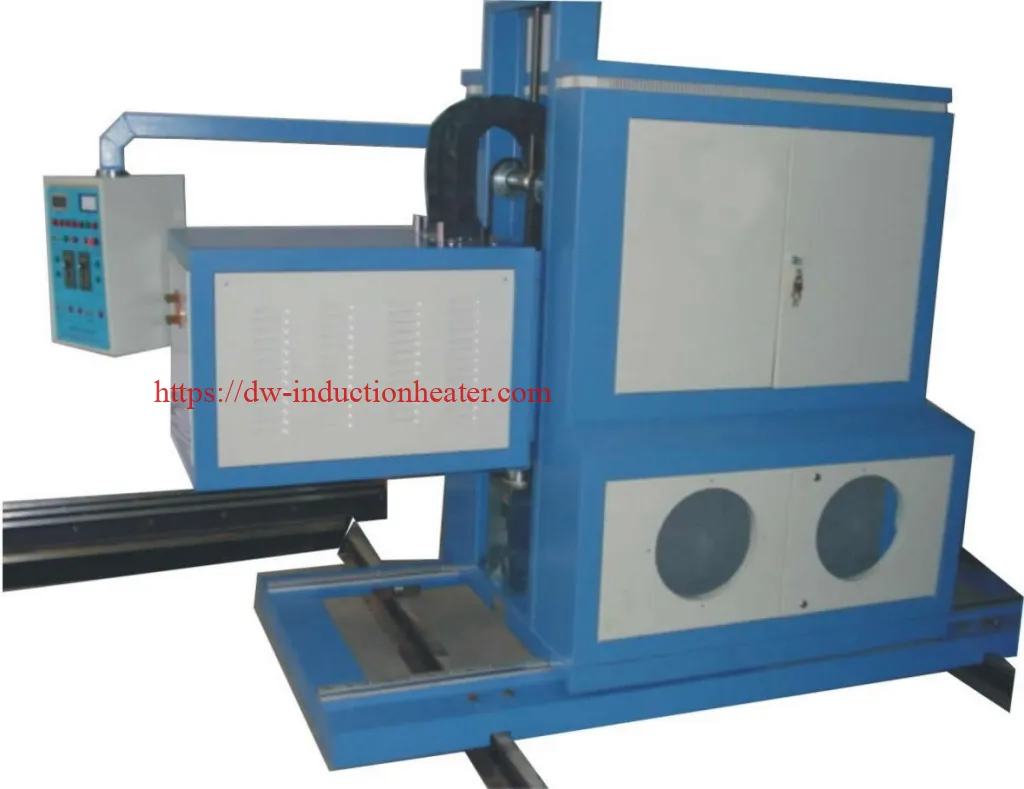
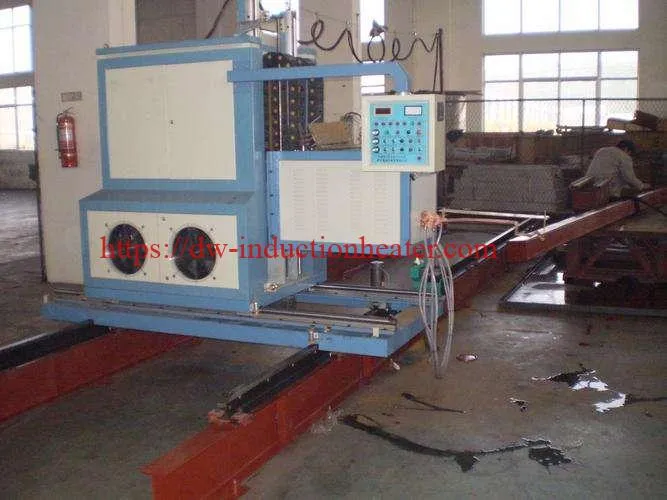
Key Components of CNC Induction Rail Hardening Machines
The efficacy of CNC induction rail hardening scanners can be attributed to their sophisticated components, which include induction coils for precise heating, quenching systems for controlled cooling, and advanced control systems. These control systems are the linchpins of the machinery, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustment of the hardening process. This level of precision ensures that the rails undergo uniform hardening, thereby maintaining their dimensional accuracy and structural integrity.
Benefits of CNC Induction Rail Hardening
The transition to CNC induction rail hardening offers a plethora of benefits over traditional furnace heating methods. Firstly, the process is markedly more energy efficient, reducing the carbon footprint associated with rail manufacturing and maintenance. Furthermore, the enhanced durability and wear resistance of the rails translate to lower maintenance costs and longer service lives, contributing to the cost-effectiveness and sustainability of railway infrastructure. Additionally, CNC induction rail hardening machines are inherently more flexible, capable of accommodating a wide range of rail profiles and compositions with minimal adjustments.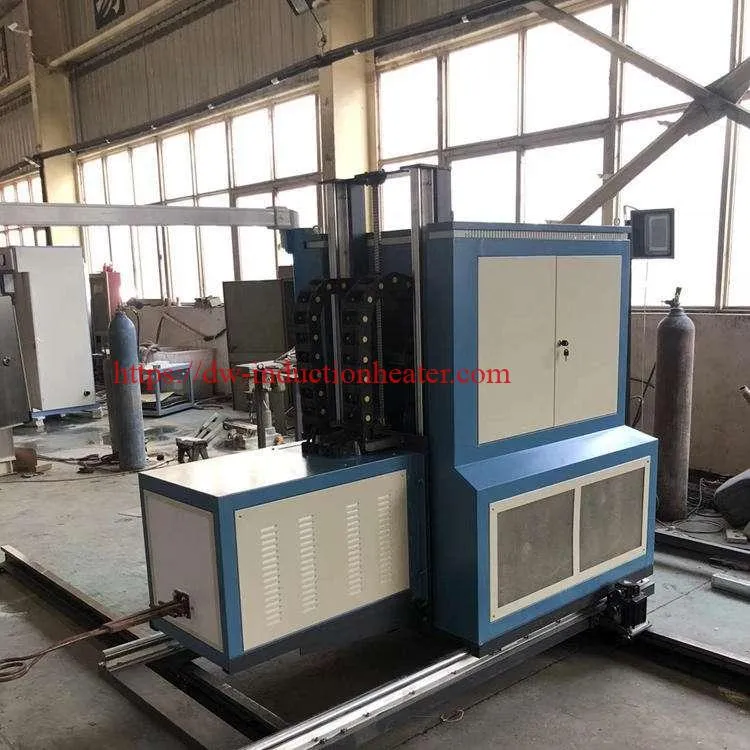
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its advantages, the induction rail hardening process is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is ensuring the compatibility of the material, as only certain steel compositions are amenable to this hardening technique. Moreover, the complexity of the machinery necessitates a high degree of expertise in operation and maintenance. However, ongoing research and development efforts are directed towards overcoming these hurdles. Innovations in machine design and control algorithms are expanding the scope of compatible materials and simplifying the operational demands of the technology.
The Future Direction of CNC Induction Rail Hardening Technology
The future of CNC induction rail hardening is replete with possibilities. Research is ongoing to further enhance the energy efficiency and environmental compatibility of the process. Efforts are also underway to broaden the range of materials that can be effectively hardened, encompassing a wider variety of steel grades and compositions. Moreover, advancements in CNC technology and control systems promise to render the process even more precise and adaptable, thereby extending the benefits of induction rail hardening to a broader array of railway applications.
Product Details:
Work-piece length ≤10000mm
Working table level travelling distance ≤11000mm
Transformer travelling distacne ≤800mm continuously adjustable
Quenching travelling speed 2 ~20mm/s continuously adjustable
Main Usage Used for all kinds of guide rail type work-piece induction quenching & induction tempering
Feature Adopting two -axial association digital control system to control transformer and working table respectively, to make sure the transform positioning accurately. Adopting advance digital tracking tech, it can program and save different kinds of treatment procedure to meet different requirements.
 The applications of CNC Induction Rail Hardening Machines include:
The applications of CNC Induction Rail Hardening Machines include:
- Enhancing the durability and wear resistance of railway tracks, leading to reduced maintenance costs and improved safety.
- Improving energy efficiency and promoting environmental sustainability in rail manufacturing and maintenance.
- Accommodating a diverse range of rail profiles and steel compositions, making the technology versatile across different railway applications.
- Ensuring dimensional accuracy and structural integrity of rails, thus enhancing the safety and reliability of railway infrastructure.
- Supporting ongoing research and development efforts to expand material compatibility, enhance energy efficiency, and reduce environmental impacts, contributing to the advancement of railway infrastructure.
Conclusion
CNC induction rail hardening systems and solutions represent a significant leap forward in railway infrastructure technology. By merging the principles of electromagnetic induction with the precision of CNC control, this technology offers a means to significantly enhance the durability, efficiency, and environmental sustainability of steel rails. While challenges remain, the ongoing research and development efforts are paving the way for a future where railways are more durable, cost-effective, and compatible with the imperatives of environmental stewardship. In this evolving industrial narrative, CNC induction rail hardening stands as a testament to the transformative power of innovation, embodying the relentless pursuit of excellence in the realm of material science and machining technology.