-
1/5
-
2/5
-
3/5
-
4/5
-
5/5
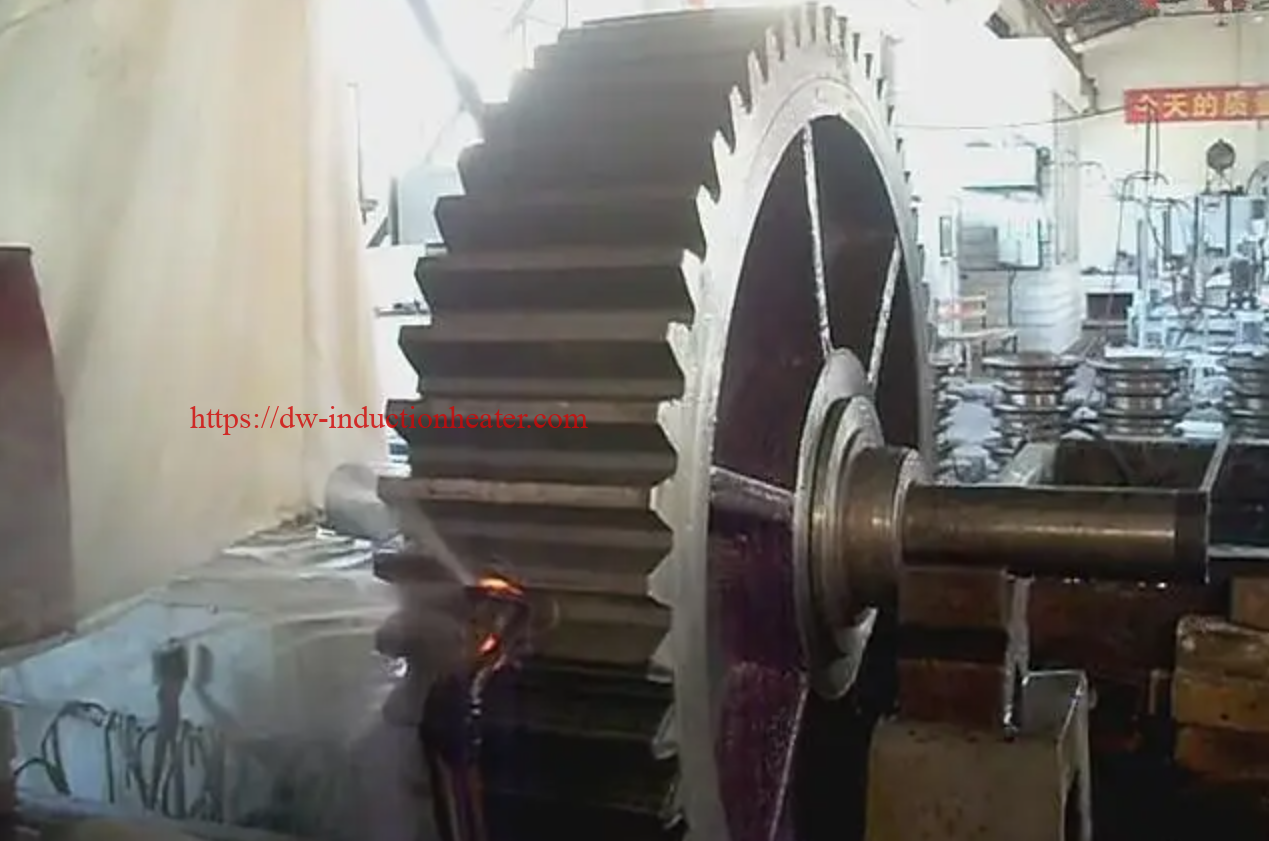
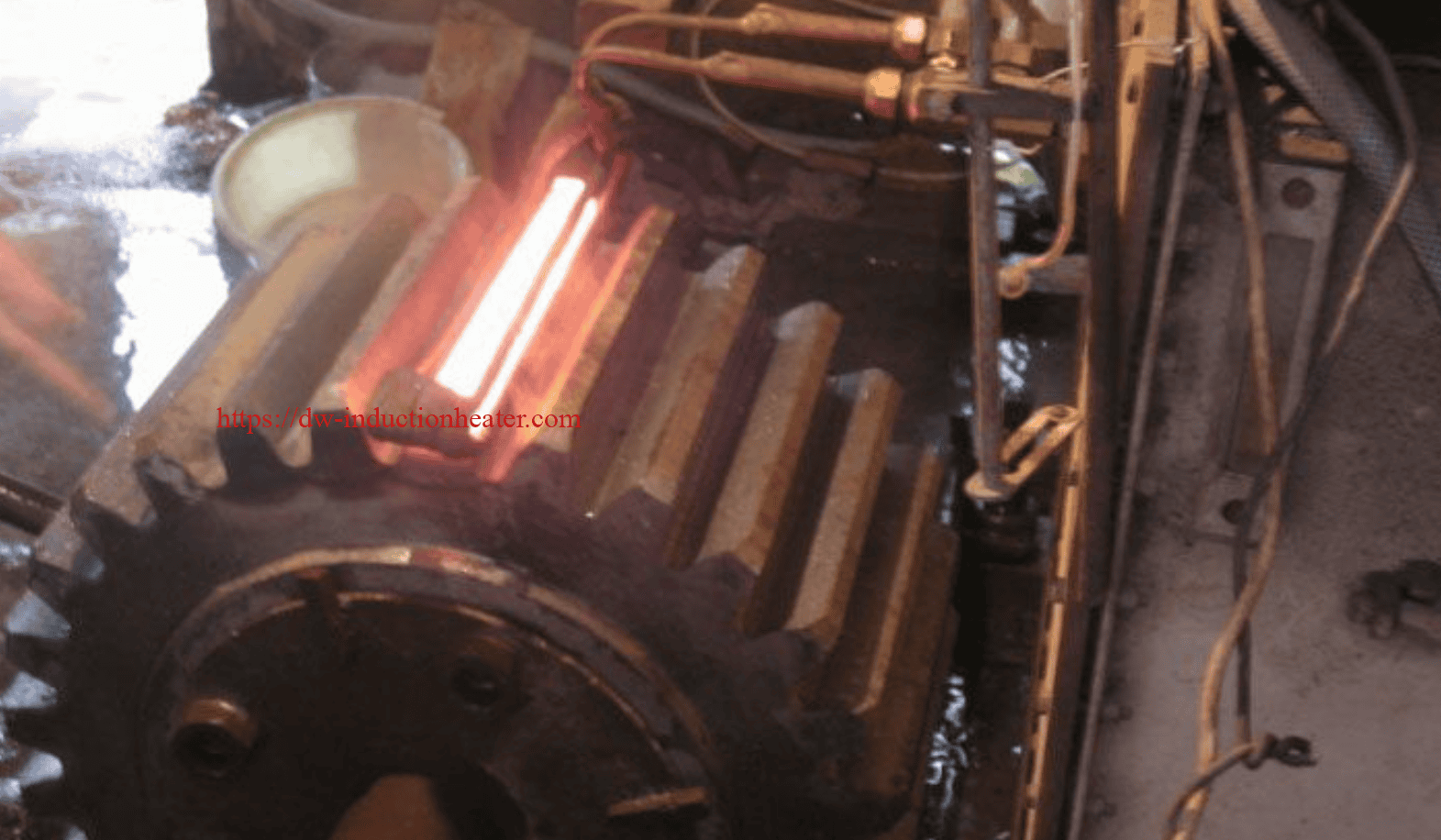
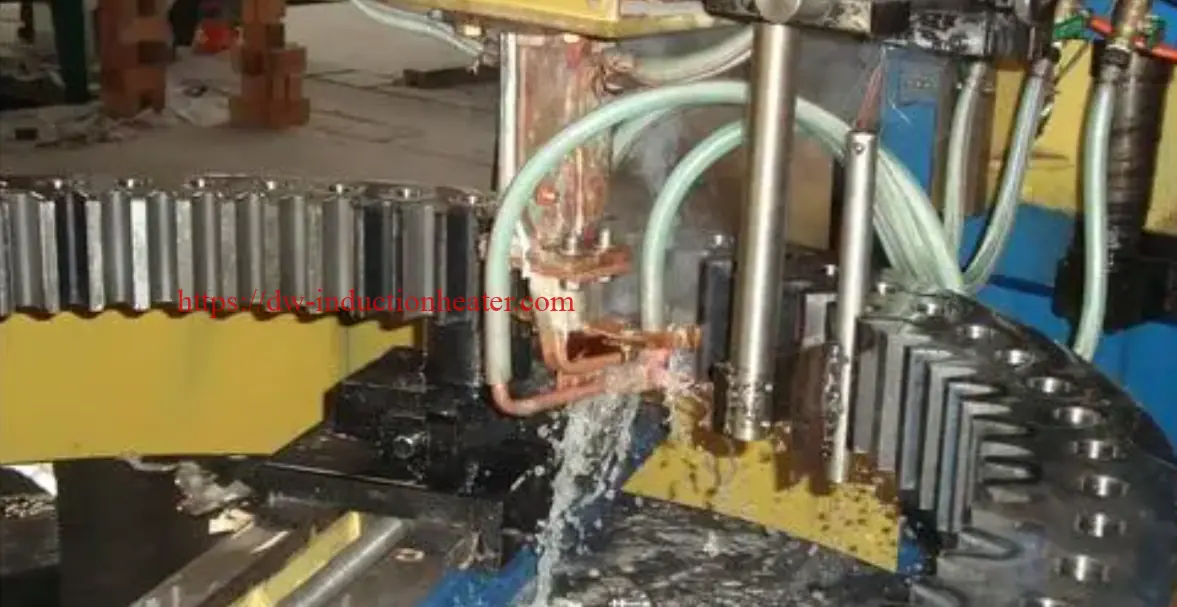
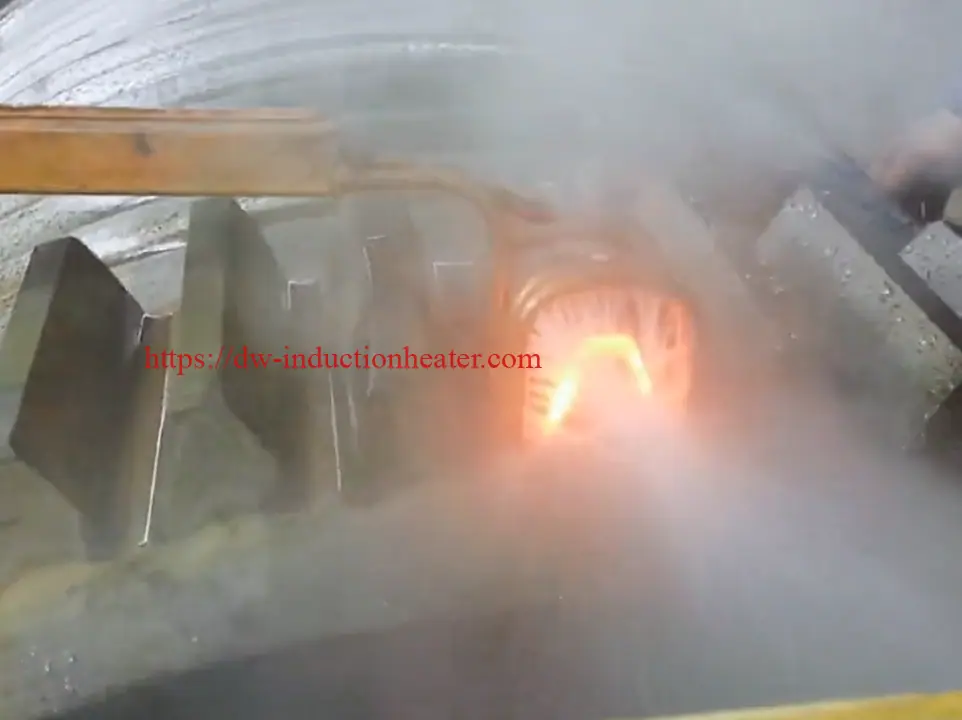
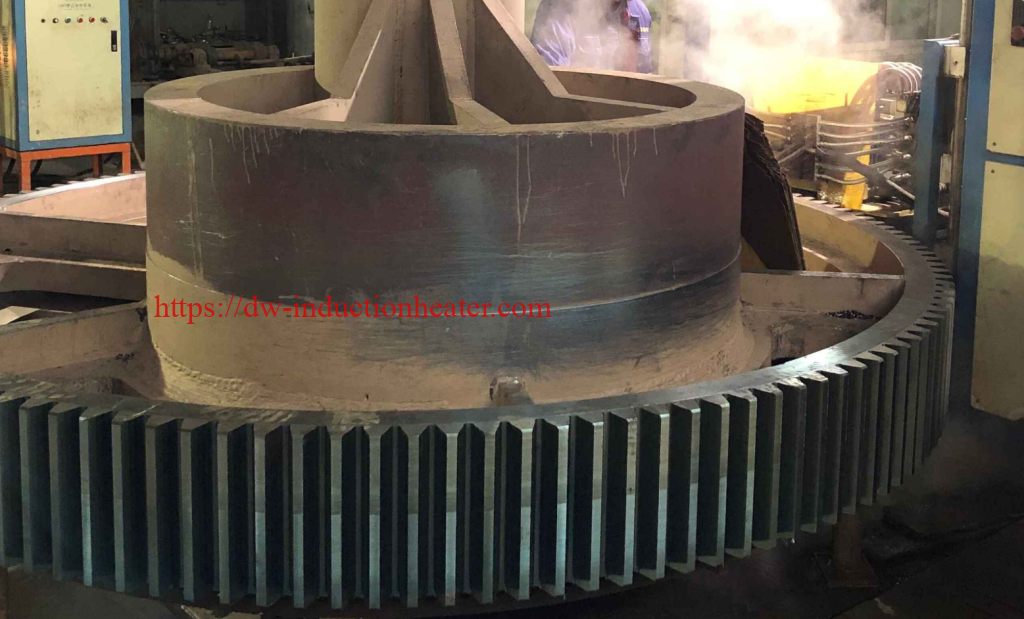
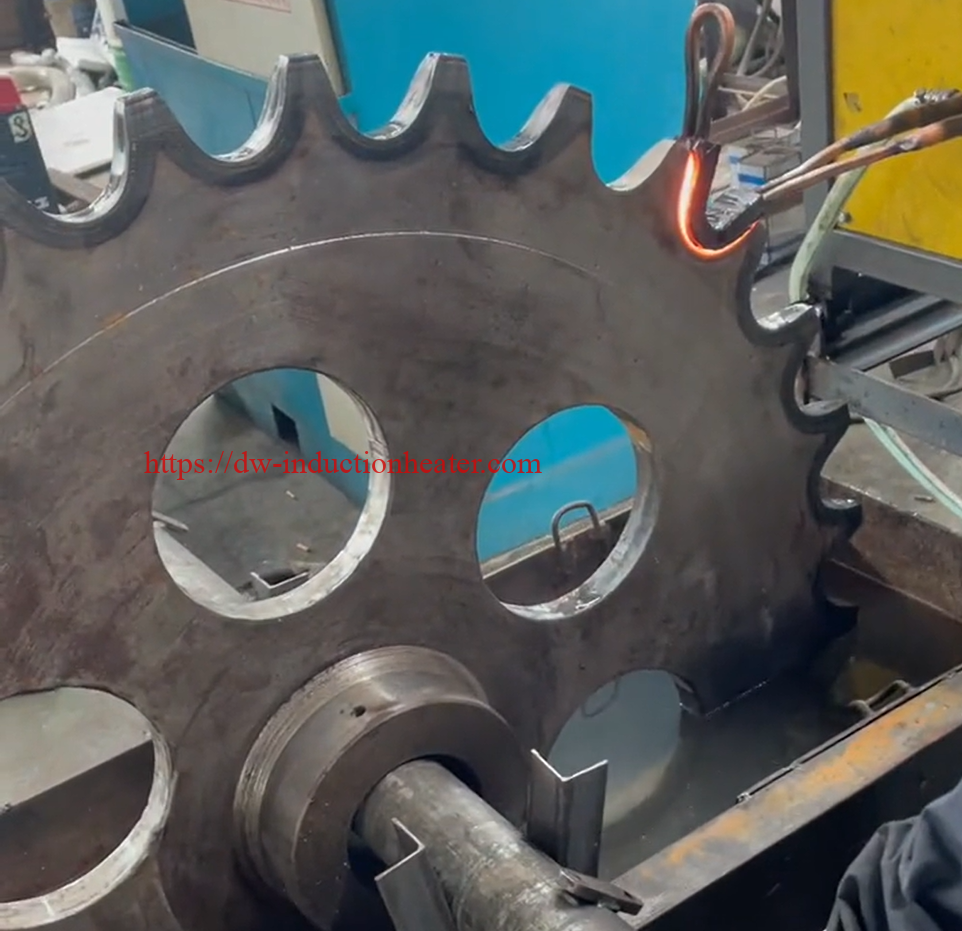
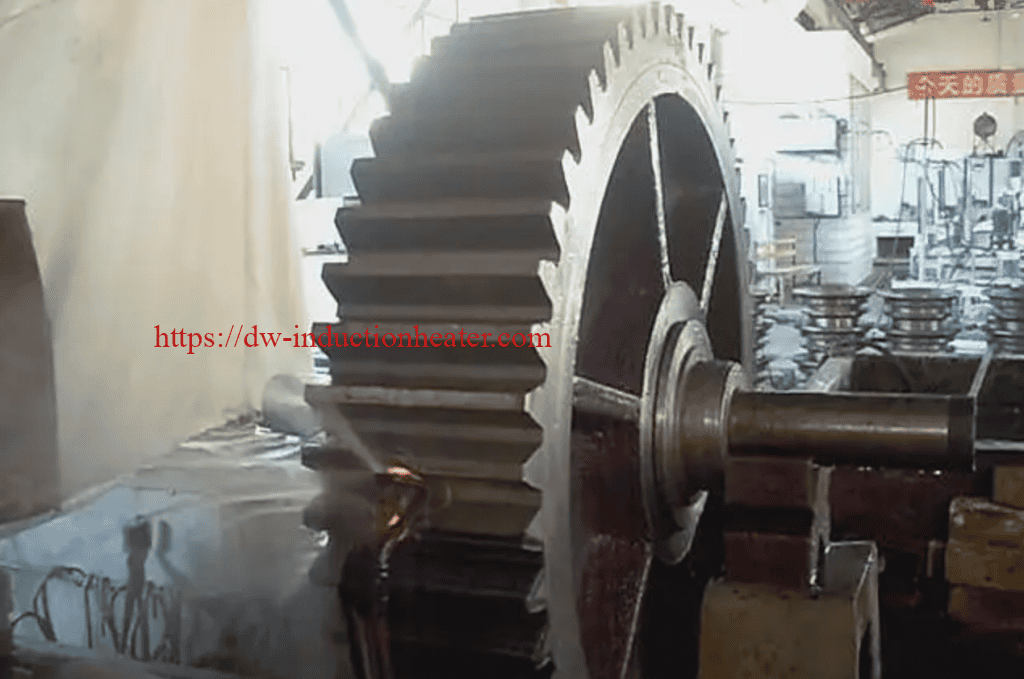
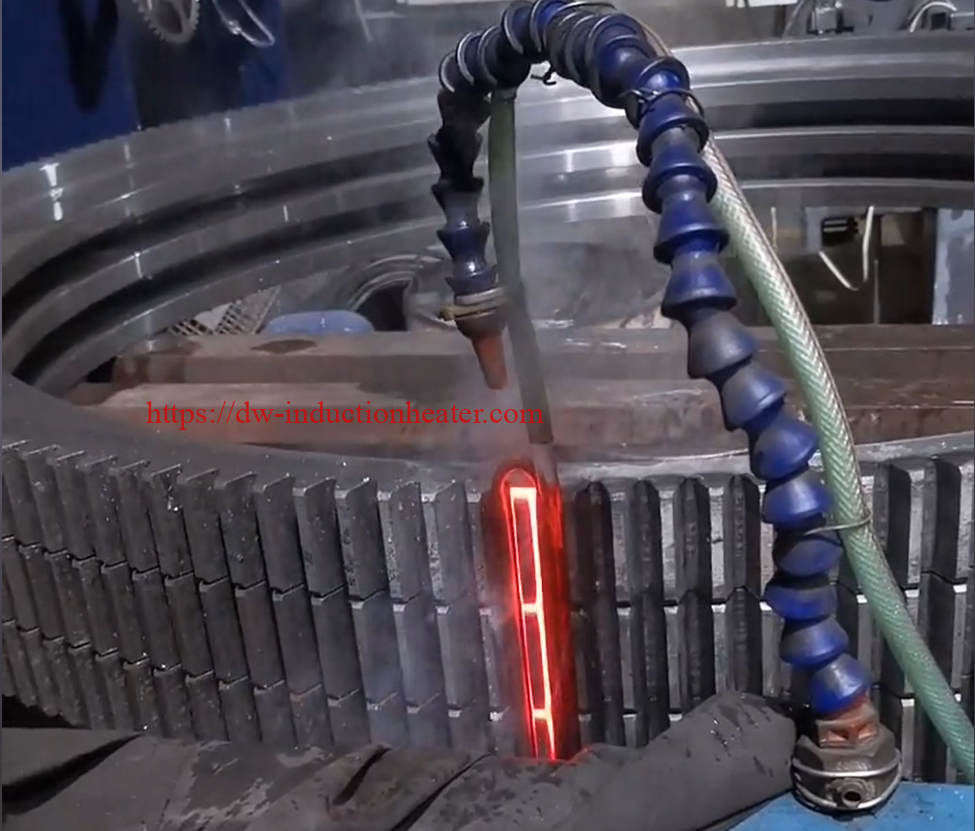
Tooth by Tooth Induction Gear Teeth Hardening Surface Process
Induction Gear Teeth Hardening: A Cost-Effective Solution for Improved Gear Performance 
Gears are an integral part of many mechanical systems, and their performance directly affects the overall efficiency and reliability of the system. One key factor that affects gear performance is the hardness of the gear teeth. Hardened gear teeth are essential for transmitting torque and power efficiently and minimizing wear and fatigue. Induction gear teeth hardening is a cost-effective solution that can significantly improve gear performance.
What is Induction Gear Teeth Hardening?
Induction gear teeth hardening is a heat treatment process that uses high-frequency induction heating to selectively harden the teeth of a gear. The process involves heating the gear teeth to a temperature above their transformation point, followed by rapid quenching to achieve the desired hardness. The result is a hardened surface layer on the gear teeth, which provides improved resistance to wear, fatigue, and pitting.
The Importance of Induction Gear Teeth Hardening
Induction gear teeth hardening is a critical process that ensures the smooth and efficient functioning of machinery. This process involves heating the gear teeth with high-frequency alternating currents and then rapidly cooling them. This results in the formation of a hardened layer that is more wear-resistant and has a longer lifespan than the original gear teeth. Induction hardening is especially important for gears because they are constantly under high stress and friction during operation.
If the gear teeth are not hardened properly, they can wear out quickly, leading to machinery breakdowns and decreased efficiency. Induction gear teeth hardening can also improve the load-carrying capacity of the gears, making them more durable and reliable in operation. By increasing the lifespan of the gears, the need for maintenance and replacements is reduced, saving time and money. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that gear teeth are properly hardened through induction hardening to ensure the smooth and efficient operation of machinery.
Advantages of Induction Gear Teeth Hardening
1. Cost-effective: Induction gear teeth hardening is a cost-effective solution compared to other hardening methods, such as carburizing or nitriding. The process is faster, requires less equipment, and produces less waste.
2. Improved gear performance: Induction gear teeth hardening improves the performance of gears by increasing their hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue resistance. This results in longer gear life and improved system efficiency.
3. Versatility: Induction gear teeth hardening can be applied to a wide range of gear sizes and shapes, including straight and helical gears, bevel gears, and worm gears.
4. Precision: Induction gear teeth hardening is a precise process that allows for selective hardening of specific areas of the gear teeth. This results in better control over the gear’s final properties and performance.
5. Environmentally friendly: Induction gear teeth hardening produces less waste and consumes less energy compared to other hardening methods. This makes it a more environmentally friendly option.
Applications of Induction Gear Teeth Hardening
Induction gear teeth hardening is used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, agriculture, and mining. It is particularly useful in applications where gears experience high loads, high speeds, or repetitive impacts. Some common applications include:
1. Transmission gears: Induction gear teeth hardening is commonly used in transmission gears to improve their wear and fatigue resistance.
2. Power generation: Gears used in power generation equipment, such as wind turbines and hydroelectric generators, can benefit from induction gear teeth hardening to improve their performance and reliability.
3. Mining equipment: Mining equipment, such as crushers and conveyor systems, rely on gears for smooth operation. Induction gear teeth hardening can improve the wear resistance of these gears, increasing their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
Materials for Induction Gear Teeth Hardening
The most common materials used for induction gear teeth hardening are carbon steels, low-alloy steels, and high-alloy steels. The choice of material depends on the application, operating conditions, and environmental factors.
Carbon steels are the most commonly used in gear manufacturing, due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication. Carbon steels can be hardened through induction heating to produce a hardened surface layer that is both hard and wear-resistant.
Low-alloy steels are used in demanding applications where high strength and toughness are required. Low-alloy steels can be hardened through induction heating to produce a hardened surface layer with exceptional wear resistance and strength.
High-alloy steels are used in the most demanding applications where extreme operating environments are experienced. Examples of such applications are in aerospace and defense industries. High-alloy steels can be hardened through induction heating to produce a hardened surface layer that is both hard and wear-resistant.
Conclusion
Induction gear teeth hardening is a critical process that ensures the reliable operation and longevity of gear wheels in various applications such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy equipment industries. The process involves the use of high-frequency induction heating to heat the surface of the gear teeth, followed by a rapid quenching process to cool the surface and produce a hardened surface layer.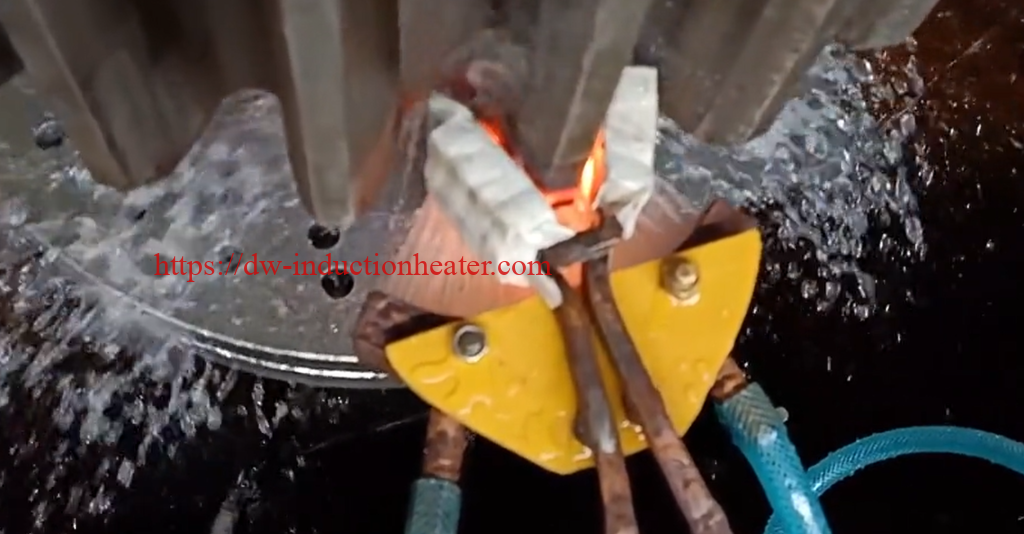
The depth of the hardened layer depends on the frequency of the induction heating equipment, the heating time, and the material used. Carbon steels, low-alloy steels, and high-alloy steels are the most commonly used materials for induction gear teeth hardening, and the choice of material depends on the application, operating conditions, and environmental factors.