Why Induction Heating is the Green Technology of the Future?
As the world continues to focus on sustainable energy and reducing carbon emissions, industries are seeking new ways to make their processes more environmentally friendly. One promising technology is induction heating, which uses magnetic fields to produce heat without the need for fossil fuels or other harmful energy sources. Induction heating is not only energy-efficient, but it is also safe, precise, and fast.
Induction heating has emerged as a sustainable and energy-efficient solution in various applications, including metal processing, automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. This advanced technology utilizes the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate heat, providing numerous environmental and economic benefits compared to traditional heating methods. This article delves into the various aspects of induction heating as a green technology, examining its advantages, applications, and future potential.
What is Induction Heating?
Induction heating is a non-contact process that uses electromagnetic fields to produce heat in a conductive material. 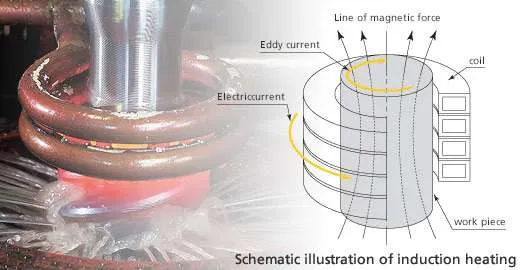 It functions by passing an alternating current (AC) through a coil, generating an electromagnetic field around the coil. When a metal object, such as a steel rod or copper tube, is placed within this field, eddy currents are induced in the material, generating heat due to the material’s electrical resistance. This targeted heating offers numerous advantages over traditional heating methods, making it an attractive option for various industries.
It functions by passing an alternating current (AC) through a coil, generating an electromagnetic field around the coil. When a metal object, such as a steel rod or copper tube, is placed within this field, eddy currents are induced in the material, generating heat due to the material’s electrical resistance. This targeted heating offers numerous advantages over traditional heating methods, making it an attractive option for various industries.
Principles of Electromagnetic Induction
The underlying principle of induction heating is Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which states that a changing magnetic field will induce an electromotive force (EMF) in a nearby conductor. This induced EMF generates eddy currents within the material, causing it to heat up. The intensity of the induced currents and the resulting heat depends on several factors, including the frequency of the alternating current, the material’s electrical conductivity and magnetic permeability, and the distance between the coil and the material.
Induction Heating Coils
The induction heating coil, also known as the inductor, is a crucial component of the induction heating system. The coil’s design and shape directly affect the efficiency and effectiveness of the heating process. Coils are typically made from materials with high electrical conductivity, such as copper or brass, and are often cooled with water or air to prevent overheating. Various coil designs are available to suit different applications, including solenoid coils, pancake coils, and multiturn coils.
Advantages of Induction Heating as a Green Technology
Induction heating offers several environmental and economic benefits compared to traditional heating methods, such as resistance heating, gas heating, and flame heating. These advantages make induction heating a green and sustainable technology for various industries.
Energy Efficiency
Induction heating is highly energy-efficient, with energy conversion efficiencies of up to 90% or more. This high efficiency is achieved by directly heating the material without any intermediate steps or heat transfer media, minimizing energy losses. In contrast, conventional heating methods often suffer from energy losses due to radiation, convection, and conduction, resulting in lower overall efficiencies.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
By utilizing electricity as the energy source, induction heating eliminates the need for fossil fuels, which are associated with greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Consequently, the technology significantly reduces the overall carbon footprint of heating processes, contributing to a cleaner environment.
Precise and Controlled Heating
Induction heating allows for precise and uniform heating of materials, enabling better control over the process parameters and resulting in higher-quality products. This precision helps reduce material wastage and rework, further enhancing the technology’s environmental benefits.
Improved Working Conditions
The non-contact nature of induction heating eliminates the need for open flames, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall safety in the workplace. Additionally, the technology produces less noise and air pollution compared to traditional heating methods, contributing to a healthier working environment.
Applications of Induction Heating in Various Industries
Induction heating’s versatility, efficiency, and environmental benefits make it an attractive option for numerous industrial applications.
Metal Processing
Induction heating is widely used in metal processing for tasks such as forging, hardening, annealing, and tempering. The technology’s precise control and rapid heating capabilities enable improved product quality and reduced energy consumption.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, induction heating is employed for processes such as brazing, curing adhesives, and shrink fitting. The technology enables faster production cycles and improved energy efficiency, contributing to greener manufacturing practices.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies on induction heating for applications such as brazing, heat treatment, and curing composites. The technology’s precise control and uniform heating capabilities are essential for producing high-quality components with tight tolerances.
Electronics Industry
Induction heating is used in the electronics industry for processes such as soldering, bonding, and curing adhesives. The technology’s rapid heating and precise temperature control contribute to improved product quality and reduced energy consumption.
Induction Heating Systems
Induction heating systems consist of several key components, including an induction heating power supply, a coil, and a workpiece. The power supply generates the alternating current, which is then passed through the coil to create the electromagnetic field. The workpiece, typically a metal object, is placed within this field, where it absorbs the energy and heats up.
Induction Heating Power Supplies
Induction heating power supplies, also known as inverters or converters, are responsible for converting the incoming electrical power into the desired frequency and voltage for the induction heating process. Modern power supplies are designed to be energy-efficient and offer advanced features such as precise temperature control, multiple heating zones, and programmable process parameters.
Induction Heating Process Control
Accurate and reliable process control is essential for achieving the desired heating results in induction heating applications. Modern induction heating systems often use advanced temperature sensors, such as infrared pyrometers or thermocouples, to monitor and control the workpiece temperature in real-time. These sensors enable precise temperature control, ensuring consistent heating results and improved product quality.
Future Potential of Induction Heating as a Green Technology
The growing emphasis on sustainability and energy conservation across various industries has created a favorable environment for the adoption of green technologies such as induction heating. Advancements in power electronics, control systems, and coil design are expected to further enhance the performance and efficiency of induction heating systems, making them an increasingly attractive option for a wide range of applications.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
The electricity-based nature of induction heating makes it an ideal technology for integration with renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. By using clean, renewable energy to power induction heating systems, industries can further reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Potential in New Applications
As induction heating technology continues to advance, new applications may emerge in areas such as food processing, medical equipment sterilization, and waste treatment. These applications can further expand the technology’s positive environmental impact and contribute to a greener future.
Conclusion
Induction heating is a green technology that offers numerous environmental and economic benefits compared to traditional heating methods. Its energy-efficient, precise, and controlled heating capabilities make it an ideal solution for various industries, including metal processing, automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly technologies continues to grow, induction heating is well-positioned to play a significant role in shaping a greener future.
