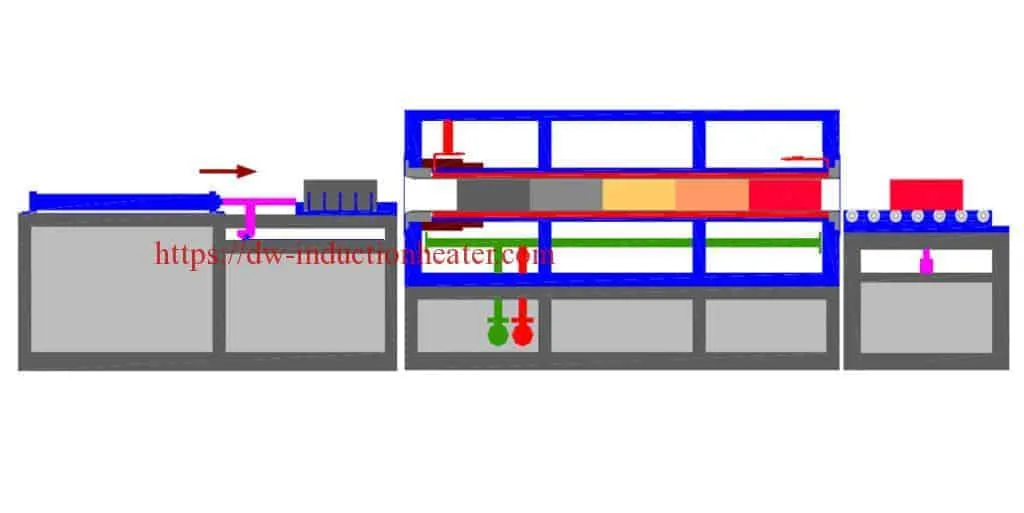
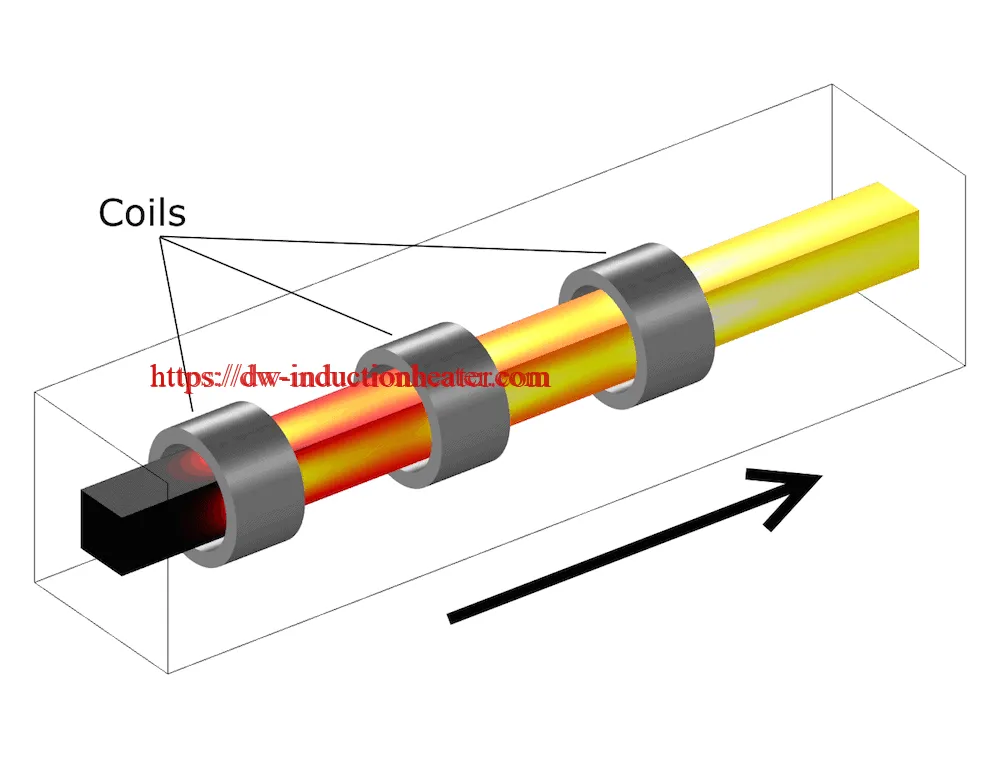
-
1/7

-
2/7
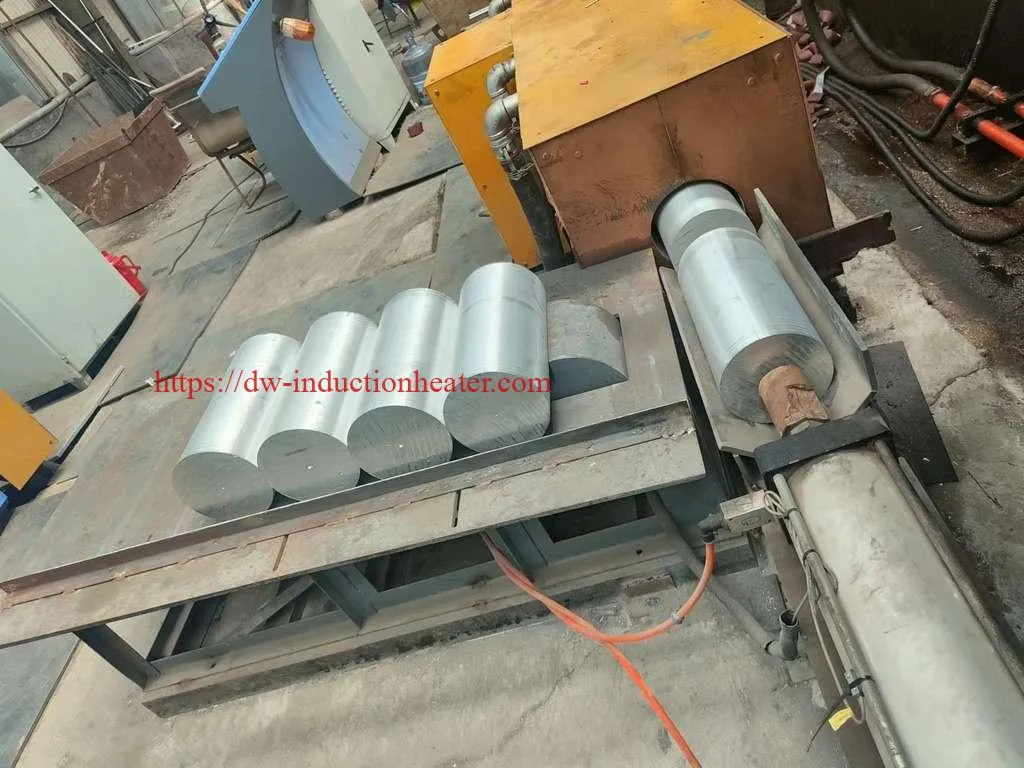

-
3/7

-
4/7

-
5/7
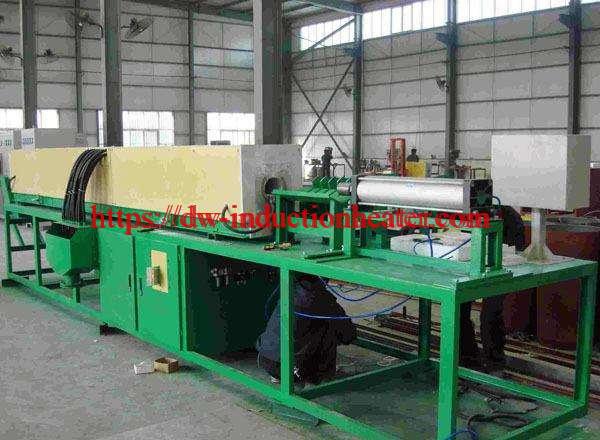

-
6/7

-
7/7
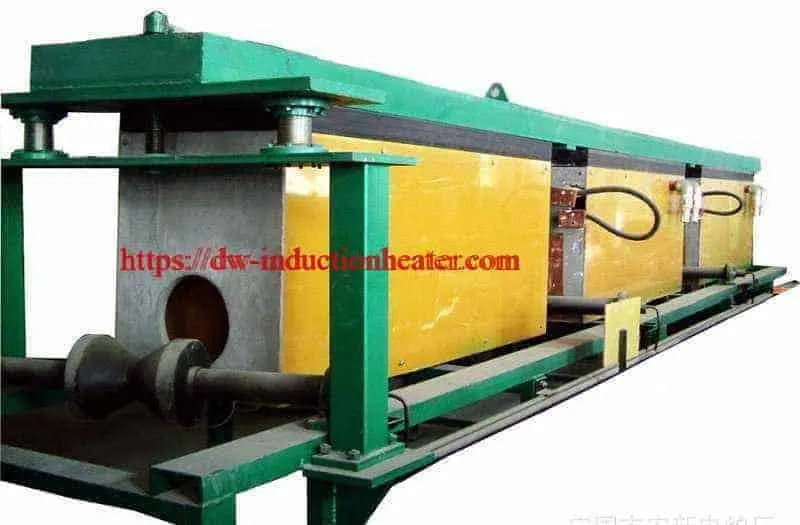

induction billet heaters for hot forming of Steel, Copper, and Aluminum
Induction Billet Heaters: Advanced Technology for Steel, Copper and Aluminum Processing
Introduction
Induction billet heaters represent a cornerstone technology in modern metal forming operations, providing precise, efficient heating solutions for steel billets, copper bars, and aluminum rods. These sophisticated systems utilize electromagnetic induction to rapidly heat metal workpieces to optimal forming temperatures without direct contact, offering significant advantages over conventional heating methods. This article explores the technical parameters, operational principles, and industrial applications of induction billet heaters across the 80kW to 1000kW power range. 
Operational Principles
Induction billet heating works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When alternating current passes through the induction coil, it generates a rapidly changing magnetic field. This field induces eddy currents within the conductive metal workpiece, generating heat through electrical resistance. The technology allows for:
- Rapid heating with minimal surface oxidation
- Precise temperature control throughout the workpiece
- Energy efficiency with up to 80% of input energy converted to useful heat
- Uniform temperature distribution for consistent forming results

Technical Parameters for Different Metals
Steel Billet Heating Parameters
| Parameter | Small Systems (80-250kW) | Medium Systems (250-500kW) | Large Systems (500-1000kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 500-3000 Hz | 300-1000 Hz | 150-600 Hz |
| Heating Capacity | 100-300 kg/hr | 300-800 kg/hr | 800-2500 kg/hr |
| Temperature Range | 900-1250°C | 900-1250°C | 900-1250°C |
| Typical Billet Size | Ø30-100mm | Ø80-180mm | Ø150-300mm |
| Power Density | 2-4 kW/kg | 1.5-3 kW/kg | 1-2.5 kW/kg |
| Heating Time | 1-5 min | 3-8 min | 5-15 min |
| Energy Consumption | 350-450 kWh/ton | 300-400 kWh/ton | 280-380 kWh/ton |
| Cooling Water Requirements | 15-40 m³/hr | 40-80 m³/hr | 80-160 m³/hr |
Copper Bar Heating Parameters
| Parameter | Small Systems (80-250kW) | Medium Systems (250-500kW) | Large Systems (500-1000kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 800-5000 Hz | 500-2000 Hz | 300-1000 Hz |
| Heating Capacity | 150-400 kg/hr | 400-1000 kg/hr | 1000-3000 kg/hr |
| Temperature Range | 700-950°C | 700-950°C | 700-950°C |
| Typical Bar Size | Ø20-80mm | Ø60-150mm | Ø120-250mm |
| Power Density | 1.5-3 kW/kg | 1.2-2.5 kW/kg | 1-2 kW/kg |
| Heating Time | 0.8-3 min | 2-6 min | 4-10 min |
| Energy Consumption | 280-380 kWh/ton | 250-350 kWh/ton | 230-320 kWh/ton |
| Cooling Water Requirements | 15-40 m³/hr | 40-80 m³/hr | 80-160 m³/hr |
Aluminum Rod Heating Parameters
| Parameter | Small Systems (80-250kW) | Medium Systems (250-500kW) | Large Systems (500-1000kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 1000-8000 Hz | 800-3000 Hz | 500-2000 Hz |
| Heating Capacity | 180-500 kg/hr | 500-1200 kg/hr | 1200-3500 kg/hr |
| Temperature Range | 400-550°C | 400-550°C | 400-550°C |
| Typical Rod Size | Ø20-80mm | Ø60-150mm | Ø120-250mm |
| Power Density | 1.2-2.5 kW/kg | 1-2 kW/kg | 0.8-1.8 kW/kg |
| Heating Time | 0.5-2 min | 1.5-4 min | 3-8 min |
| Energy Consumption | 220-300 kWh/ton | 200-280 kWh/ton | 180-260 kWh/ton |
| Cooling Water Requirements | 15-40 m³/hr | 40-80 m³/hr | 80-160 m³/hr |
System Components and Technical Specifications
Power Supply System
| Component | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 380-480V, 3-phase | Higher voltages available for large systems |
| Input Frequency | 50/60 Hz | Grid standard |
| Power Factor | 0.92-0.98 | With power factor correction |
| Efficiency | 85-95% | Conversion efficiency |
| Cooling Method | Water-cooled | Closed-loop deionized water system |
| Control Interface | PLC with HMI touchscreen | Industry 4.0 compatible |
| Protection Class | IP54 (control cabinet) | Higher protection available |
Induction Coil Specifications
| Parameter | Steel Billets | Copper Bars | Aluminum Rods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coil Material | Copper tubing | Copper tubing | Copper tubing |
| Coil Cooling | Pressurized water | Pressurized water | Pressurized water |
| Coil Design | Multi-turn helical | Multi-turn helical | Multi-turn helical |
| Insulation | Ceramic/refractory | Ceramic/refractory | Ceramic/refractory |
| Coil Lifespan | 8,000-15,000 hours | 10,000-18,000 hours | 12,000-20,000 hours |
| Coupling Efficiency | 70-85% | 75-90% | 80-92% |
 Cooling System Requirements
Cooling System Requirements
| Power Rating | Water Flow Rate | Heat Exchanger Capacity | Pump Power | Water Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80-250kW | 15-40 m³/hr | 70-220kW | 3-7.5kW | <20μS/cm conductivity |
| 250-500kW | 40-80 m³/hr | 220-450kW | 7.5-15kW | <20μS/cm conductivity |
| 500-1000kW | 80-160 m³/hr | 450-900kW | 15-30kW | <20μS/cm conductivity |
Material-Specific Considerations
Steel Billet Processing
Steel billets typically require the highest processing temperatures among common metals, reaching 1200-1250°C for hot forming operations. The magnetic properties of steel below the Curie point (approximately 768°C) significantly affect the induction heating process:
- Initial heating phase: Lower efficiency due to magnetic properties
- Above Curie point: Efficiency improves as steel becomes non-magnetic
- Temperature uniformity: Critical for preventing defects in formed products
- Typical applications: Forging, rolling, extrusion, and wire drawing
Copper Bar Processing
Copper’s high electrical conductivity presents unique challenges for induction heating:
- Higher frequencies required for effective heating compared to steel
- Excellent thermal conductivity aids temperature uniformity
- Typical processing temperatures: 700-950°C depending on alloy composition
- Oxide formation must be minimized through protective atmospheres or rapid processing
- Common applications: Extrusion, rolling, and forging for electrical components
Aluminum Rod Processing
Aluminum requires careful temperature control due to its relatively low melting point:
- Precise temperature control essential to prevent melting (660°C for pure aluminum)
- Typical processing temperatures: 400-550°C
- Higher frequencies required due to aluminum’s electrical conductivity
- Rapid heating possible due to lower heat content requirements
- Applications: Extrusion, forging, and drawing for automotive and aerospace components
Control Systems and Automation
Modern induction billet heaters incorporate sophisticated control systems:
- PLC-based control with touchscreen HMI interfaces
- Pyrometer-based temperature measurement and feedback control
- Automatic power adjustment based on material properties and sizes
- Recipe management for different alloys and product dimensions
- Data logging and quality assurance reporting
- Remote monitoring and integration with plant management systems
- Predictive maintenance capabilities
Energy Efficiency Considerations
| System Size | Power Consumption | Energy Efficiency | CO₂ Reduction vs Gas Heating |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80-250kW | 70-225kW effective | 75-85% | 30-40% |
| 250-500kW | 225-450kW effective | 80-88% | 35-45% |
| 500-1000kW | 450-900kW effective | 82-90% | 40-50% |
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Induction billet heaters in the 80kW to 1000kW range offer versatile, efficient solutions for heating steel billets, copper bars, and aluminum rods in modern metal forming operations. The technology’s precise temperature control, energy efficiency, and minimal environmental impact make it increasingly the preferred choice for advanced manufacturing facilities. As metal forming industries continue to evolve toward more sustainable and efficient processes, induction heating technology will undoubtedly play a central role in meeting these objectives.