-
1/4

-
2/4

-
3/4
-
4/4
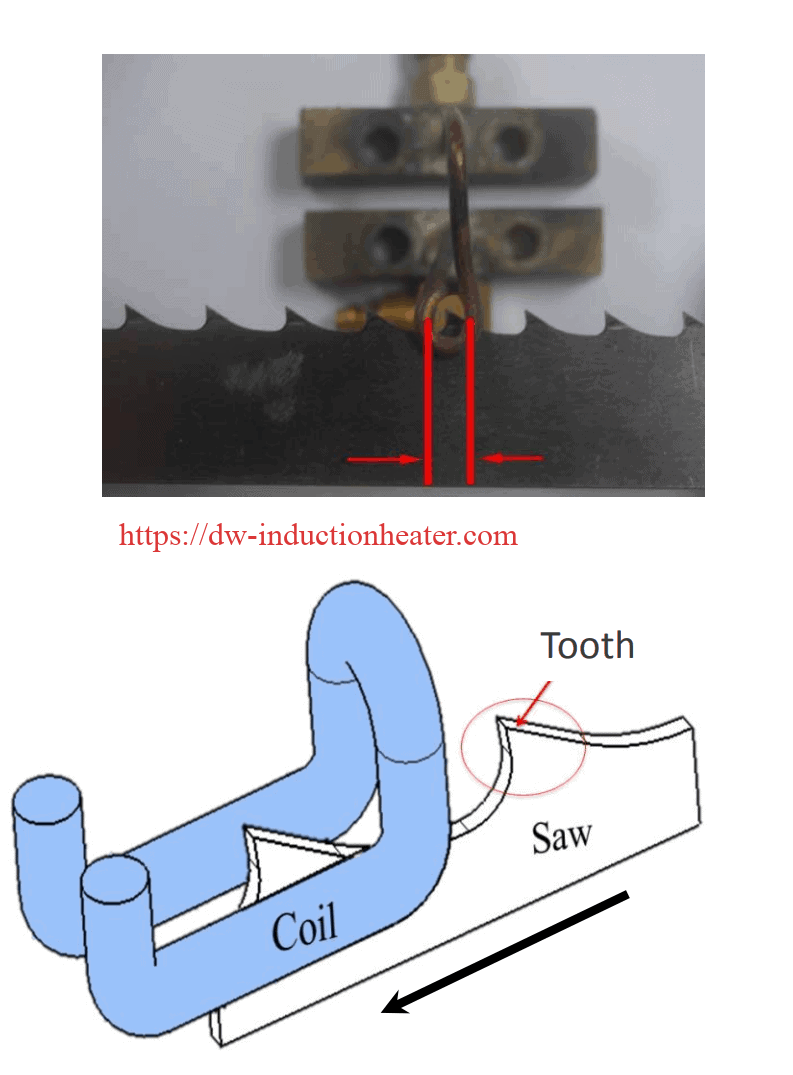
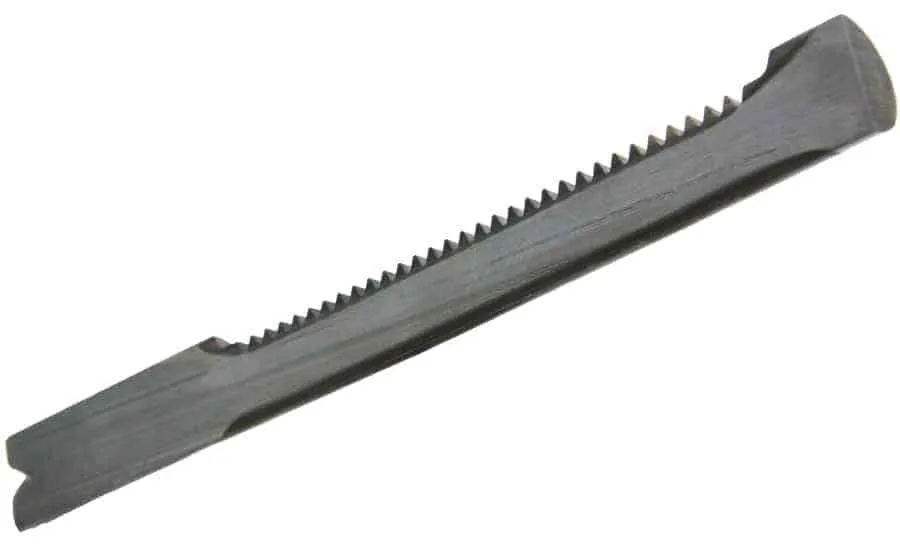
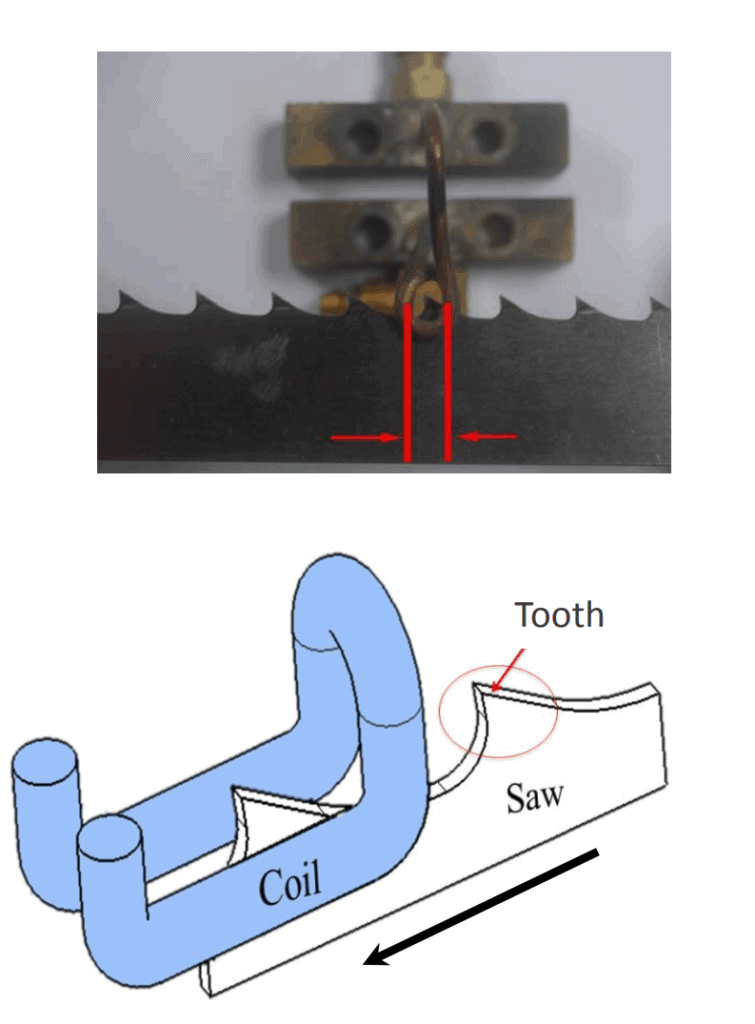
Induction hardening saw teeth of blade
Induction hardening saw teeth of blade
Method of induction hardening the teeth of a steel saw blade composed of “high speed tool steel,” which comprises passing a high frequency induction current through the teeth of the blade so that all the particles of the teeth, both on the surface and in the interior thereof, are heated to the critical temperature of approximately 2375″ F. without similarly heating other portions of the blade, controlling the frequency and magnitude of the induced current so that substantially all of the carbides in the teeth are in condition to dissolve in the austenitic matrix practically as soon as the steel reaches the critical temperature, and thereupon cooling the teeth to a temperature substantially below the critical temperature before substantial grain growth occurs; instead of either hardening the entire blade or merely induction surface hardening the teeth.
Induction hardening saw teeth of blade for a hardening application; the objective is to reduce the heating time
Material : Section of the saw blade
Temperature: 1650 ºF (899 ºC)
Frequency : 134 kHz
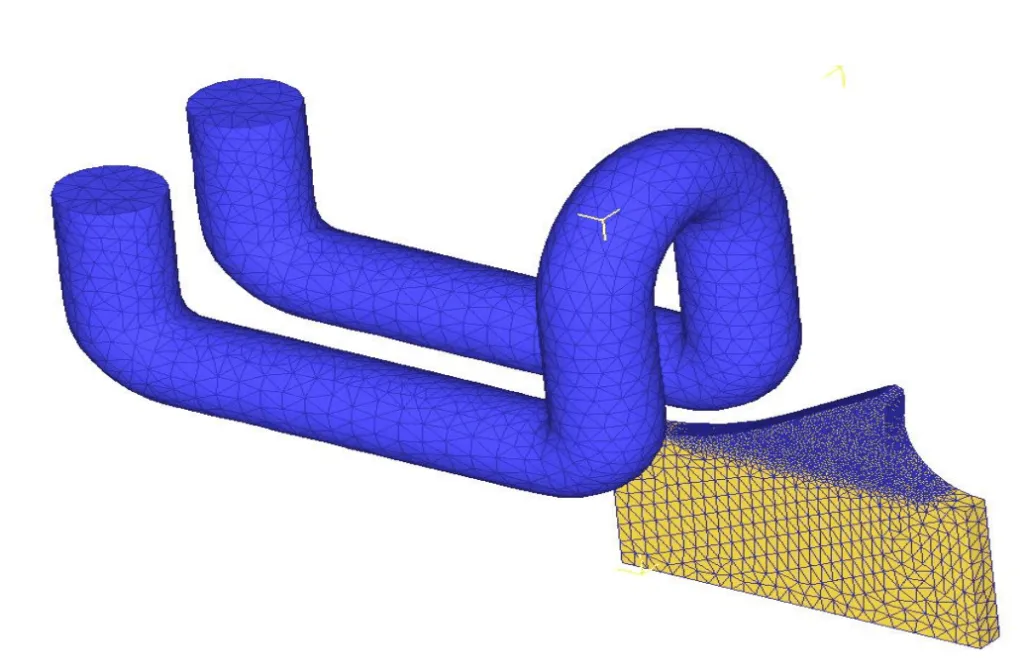
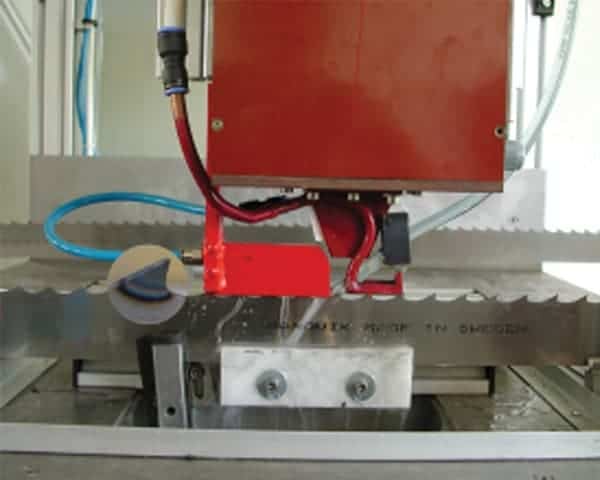
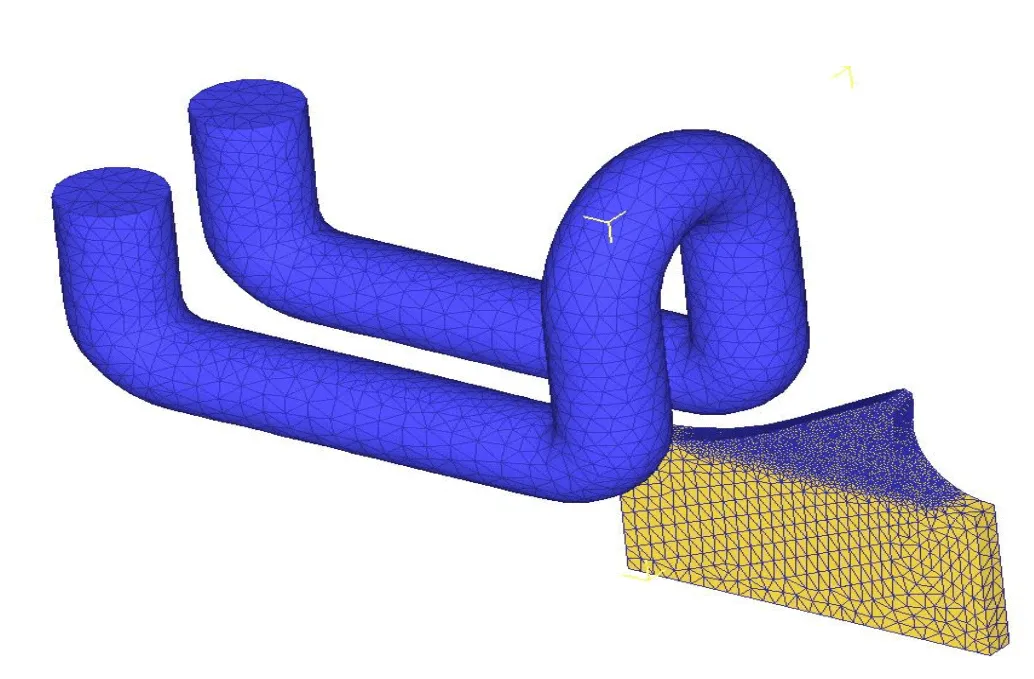
Equipment : DW-UHF-30kW 50-150 kHz induction heating system equipped with a remote workhead containing eight 1.0 μF capacitors.A multiple position two-turn helical induction heating coil designed and developed specifically for this application
The induction heating coil was developed so that it would not concentrate heat in the outside edge valley of the tooth. The part was placed under the coil approximately 1/8” (3.2 mm) away and the power was turned on. With the 30 kW DW-UHF induction heating power supply the part heated to temperature within the targeted rate of five teeth per
four seconds.
Results/Benefits
Speed: The customer was already using induction, but wanted to upgrade to a higher power system to increase
their production rate (Prior to first using induction from HLQ, the client used a torch.)
Precision and Repeatability: A torch isn’t as precise as induction nor is it repeatable, whereas induction can be
implemented to be highly repeatable
Efficiency: Induction hardening uses less energy than a torch and offers instant on/off heating