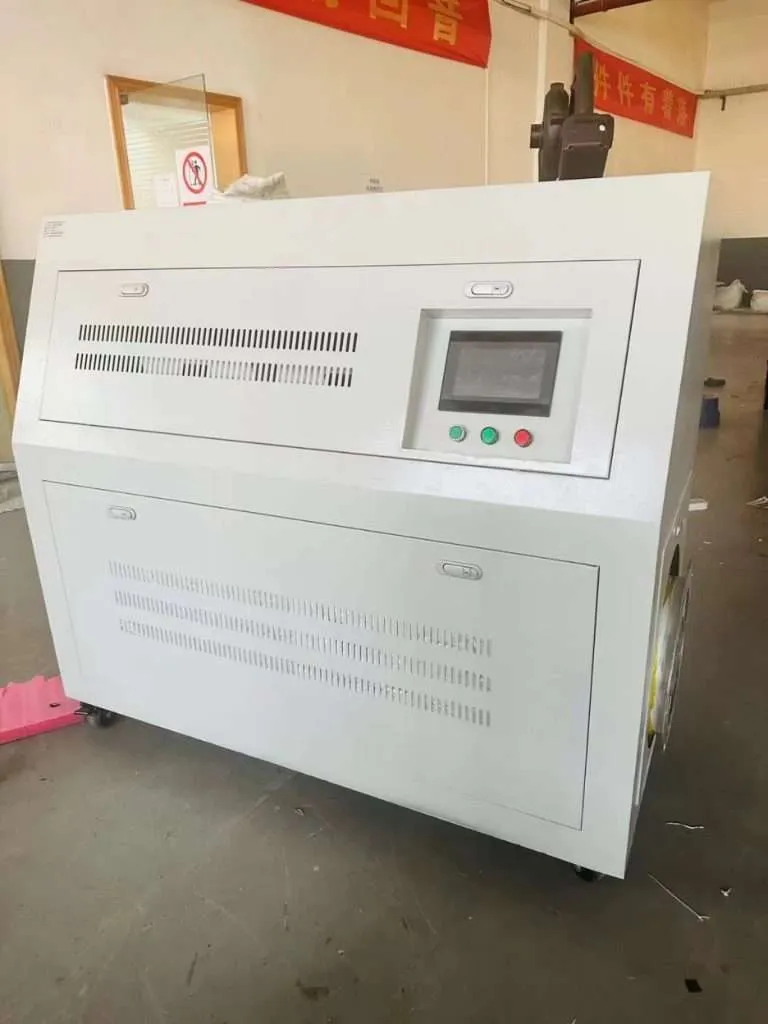
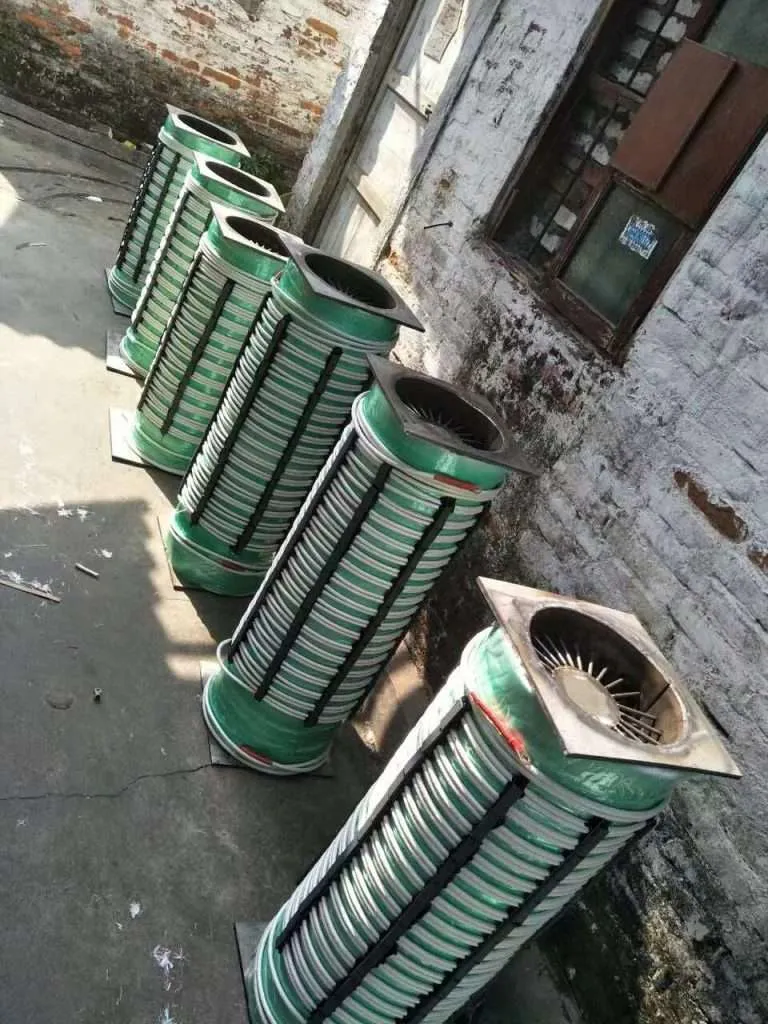
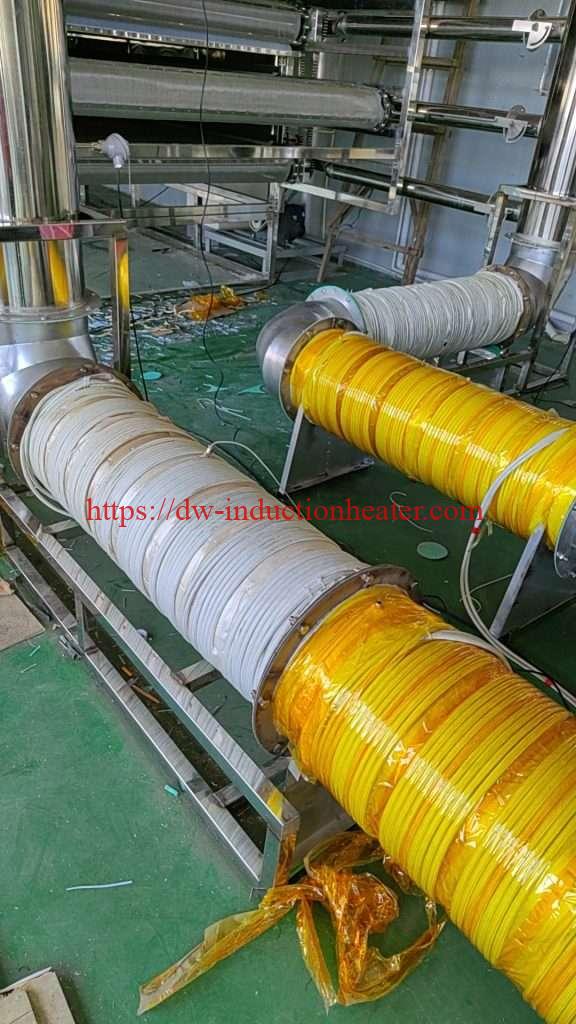
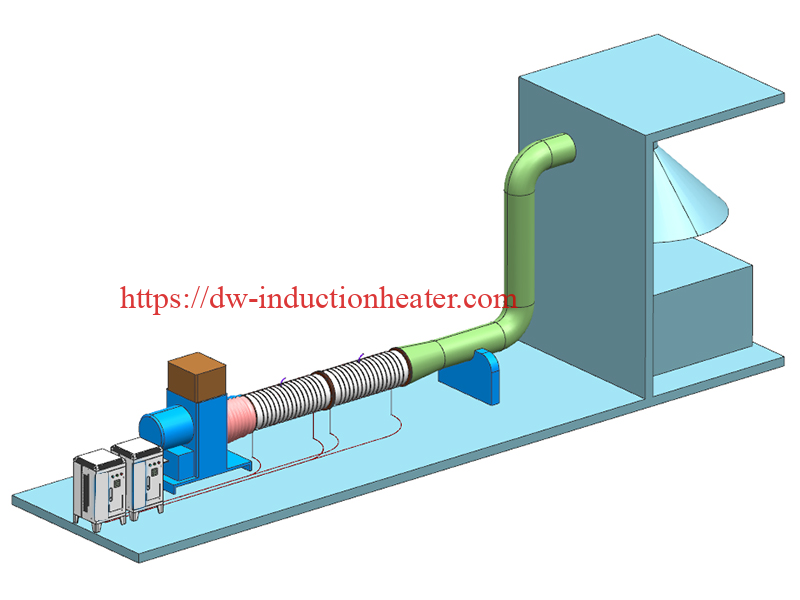
The Ultimate Guide to Induction Hot Air Heaters: Efficient, Safe, and Versatile Heating Solutions
Introduction:
In today’s world, where energy efficiency and safety are paramount, induction hot air heaters have emerged as a popular choice for both industrial and residential applications. These innovative heating systems utilize the principles of electromagnetic induction to generate heat, offering a range of benefits over traditional heating methods. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of induction hot air heaters, exploring their working principles, advantages, applications, and key considerations when choosing the right heater for your needs.
Section 1: Understanding Induction Hot Air Heaters
1.1 What is an Induction Hot Air Heater?
An induction hot air heater is a modern heating device that uses electromagnetic induction to generate heat. Unlike conventional heating systems that rely on resistance or combustion, induction heaters create heat by inducing eddy currents in a conductive material, such as a metal workpiece or a specially designed heating element. This process is highly efficient, as the heat is generated directly within the material itself, minimizing energy losses.
1.2 The Science Behind Induction Heating
Induction heating is based on the principles of electromagnetism. When an alternating current is passed through a coil, it creates a magnetic field around it. If a conductive material is placed within this magnetic field, the alternating magnetic field induces eddy currents within the material. These eddy currents flow through the material’s electrical resistance, generating heat due to the Joule effect. The amount of heat generated depends on factors such as the frequency of the alternating current, the strength of the magnetic field, and the properties of the conductive material.
1.3 Key Components of an Induction Hot Air Heater
An induction hot air heater consists of several essential components that work together to generate and distribute heat efficiently:
a. Induction Coil: The induction coil is the heart of the heater. It is typically made of copper and is designed to create a strong magnetic field when an alternating current is passed through it.
b. Heating Element: The heating element is a conductive material, usually a metal with high magnetic permeability, that is placed within the induction coil’s magnetic field. The eddy currents induced in the heating element generate heat.
c. Power Supply: The power supply provides the alternating current necessary to create the magnetic field in the induction coil. It controls the frequency and power output of the heater.
d. Blower or Fan: A blower or fan is used to circulate the heated air, distributing it evenly throughout the desired space.
e. Control System: The control system regulates the heater’s operation, allowing users to adjust temperature settings, timers, and other parameters for optimal performance and safety.
Section 2: Advantages of Induction Hot Air Heaters
Induction hot air heaters offer several significant advantages over traditional heating methods, making them an attractive choice for various applications.
2.1 Energy Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of induction hot air heaters is their exceptional energy efficiency. Unlike resistance heating, where energy is lost through heat dissipation, induction heating generates heat directly within the target material. This direct heating minimizes energy losses, resulting in efficiency levels of up to 90-95%. By consuming less energy to achieve the desired temperature, induction heaters can lead to substantial cost savings in the long run.
2.2 Rapid Heating
Induction hot air heaters are known for their ability to generate heat quickly. The electromagnetic induction process allows for near-instantaneous heat generation, as the eddy currents are induced directly within the heating element. This rapid heating capability is particularly advantageous in applications where fast temperature ramp-up is required, such as in industrial processes or for quick room heating.
2.3 Precise Temperature Control
Induction hot air heaters offer precise temperature control, enabling users to maintain consistent and uniform heating. The power output of the heater can be easily adjusted to achieve the desired temperature, and advanced control systems can maintain the temperature within a narrow range. This level of precision is crucial in applications where temperature consistency is critical, such as in manufacturing processes or laboratory settings.
2.4 Enhanced Safety
Induction hot air heaters provide a safer heating alternative compared to traditional methods. Since the heat is generated within the heating element itself, there are no exposed heating surfaces or open flames. This eliminates the risk of accidental burns or fires, making induction heaters suitable for use in environments where safety is a top priority. Additionally, induction heaters do not produce any harmful emissions or fumes, ensuring a clean and safe working environment.
2.5 Durability and Low Maintenance
Induction hot air heaters are built to last, with robust construction and minimal moving parts. The absence of direct contact between the induction coil and the heating element reduces wear and tear, extending the heater’s lifespan. Moreover, induction heaters require minimal maintenance compared to other heating systems. There are no heating elements to replace, and the absence of combustion eliminates the need for regular cleaning or servicing of burners or filters.
2.6 Versatility
Induction hot air heaters are highly versatile and can be adapted to suit a wide range of applications. They can be designed in various sizes and configurations to meet specific heating requirements, from small portable units for localized heating to large-scale industrial systems. Induction heaters can also be integrated into existing processes or equipment, making them a flexible choice for retrofitting or upgrading heating systems.
Section 3: Applications of Induction Hot Air Heaters
Induction hot air heaters find applications across diverse industries and sectors, thanks to their efficient and reliable heating performance.
3.1 Industrial Applications
a. Manufacturing Processes: Induction hot air heaters are extensively used in manufacturing processes that require precise and uniform heating. They are ideal for applications such as drying, curing, and heat treatment of materials like metals, plastics, and composites.
b. Automotive Industry: In the automotive industry, induction heaters are employed for various purposes, including paint drying, adhesive curing, and preheating of metal components prior to welding or forming.
c. Food Processing: Induction hot air heaters are used in the food processing industry for drying, roasting, and sterilization applications. They provide uniform heating and precise temperature control, ensuring consistent product quality.
3.2 Commercial Applications
a. Warehouses and Storage Facilities: Induction hot air heaters are used to maintain optimal temperatures in warehouses and storage facilities, preventing damage to stored goods and ensuring a comfortable working environment for employees.
b. Greenhouses and Agricultural Facilities: Induction heaters are employed in greenhouses and agricultural facilities to provide efficient and controllable heating, promoting plant growth and protecting crops from cold temperatures.
c. Event Spaces and Tents: Portable induction hot air heaters are popular for heating event spaces, tents, and temporary structures. They offer quick and efficient heating without the need for extensive installation or ventilation.
3.3 Residential Applications
a. Home Heating: Induction hot air heaters can be used as a primary or supplementary heating source in residential settings. They provide efficient and targeted heating, allowing homeowners to warm specific areas or rooms as needed.
b. Garages and Workshops: Induction heaters are ideal for heating garages and workshops, providing a comfortable working environment and preventing equipment from being affected by cold temperatures.
c. Outdoor Living Spaces: Portable induction hot air heaters can be used to extend the usability of outdoor living spaces, such as patios and decks, during colder months. They offer a safe and efficient way to provide warmth without the need for open flames or gas lines.
Section 4: Choosing the Right Induction Hot Air Heater
When selecting an induction hot air heater, there are several key factors to consider to ensure optimal performance and suitability for your specific application.
4.1 Heating Capacity and Coverage Area
The first step in choosing an induction hot air heater is to determine the required heating capacity and coverage area. Consider the size of the space you need to heat, as well as the desired temperature range. Induction heaters come in various sizes and power ratings, so it’s essential to select a unit that can efficiently heat your specific space.
4.2 Power Source and Efficiency
Induction hot air heaters are available in different power configurations, including electric and gas-powered models. Electric induction heaters are more common and offer higher efficiency levels, as they convert electrical energy directly into heat. Gas-powered induction heaters, while less efficient, may be preferred in areas where electricity is limited or expensive. Consider the available power sources and the long-term operating costs when making your selection.
4.3 Portability and Installation Requirements
Depending on your application, portability and ease of installation may be important factors to consider. Portable induction hot air heaters are ideal for temporary or mobile heating needs, such as in event spaces or construction sites. They are easy to set up and can be moved as required. For permanent installations, consider the heater’s size, mounting options, and any necessary electrical or ventilation requirements.
4.4 Safety Features
Safety should be a top priority when choosing an induction hot air heater. Look for models that incorporate advanced safety features, such as automatic shut-off mechanisms, overheat protection, and tip-over switches. These features ensure that the heater operates safely and minimizes the risk of accidents or fires. Additionally, consider the heater’s certification and compliance with relevant safety standards.
4.5 Control and Automation
Modern induction hot air heaters often come equipped with sophisticated control systems that allow for precise temperature regulation and automation. Look for models with user-friendly interfaces, programmable thermostats, and remote control capabilities. These features enable you to optimize the heater’s performance, set schedules, and adjust settings conveniently.
4.6 Maintenance and Durability
Consider the maintenance requirements and durability of the induction hot air heater. Opt for models with robust construction and high-quality components to ensure long-lasting performance. Induction heaters with minimal moving parts and easy access for cleaning and servicing can help reduce maintenance costs and downtime.
4.7 Cost and Return on Investment
While the initial cost of an induction hot air heater may be higher compared to traditional heating methods, it’s essential to consider the long-term return on investment. The energy efficiency and low maintenance requirements of induction heaters can result in significant cost savings over time. Evaluate the heater’s life cycle costs, including energy consumption, maintenance expenses, and potential productivity gains, to determine the overall value proposition.
Section 5: Best Practices for Using Induction Hot Air Heaters
To maximize the performance and longevity of your induction hot air heater, follow these best practices:
5.1 Proper Sizing and Placement
Ensure that the induction heater is properly sized for your specific space and heating requirements. Overloading or undersizing the heater can lead to inefficient operation and reduced lifespan. Position the heater strategically to optimize heat distribution and avoid obstructions that may hinder airflow.
5.2 Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
While induction hot air heaters require minimal maintenance, regular cleaning and inspections can help prolong their lifespan. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning the heater’s exterior and any accessible internal components. Regularly check for signs of wear, damage, or malfunction, and address any issues promptly.
5.3 Temperature Control and Monitoring
Use the heater’s control system to maintain the desired temperature range accurately. Avoid excessive temperature fluctuations, as they can strain the heater and reduce its efficiency. Monitor the temperature regularly to ensure consistent and optimal performance.
5.4 Proper Ventilation
Although induction hot air heaters do not produce harmful emissions, proper ventilation is still important to maintain air quality and prevent the buildup of stale air. Ensure that the heated space has adequate ventilation, especially in enclosed or poorly ventilated areas.
5.5 Safety Precautions
Always follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines when operating an induction hot air heater. Keep flammable materials away from the heater, and ensure that the unit is placed on a stable and level surface. Do not cover or obstruct the heater’s air intake or output vents. Regularly inspect electrical connections and cables for any signs of damage or wear.
Conclusion:
Induction hot air heaters offer a highly efficient, safe, and versatile heating solution for a wide range of applications. By harnessing the power of electromagnetic induction, these heaters provide rapid, precise, and uniform heating while minimizing energy losses and maintenance requirements. Whether you need efficient heating for industrial processes, commercial spaces, or residential comfort, induction hot air heaters are a compelling choice.
When selecting an induction heater, consider factors such as heating capacity, power source, portability, safety features, control options, and long-term cost-effectiveness. By following best practices for installation, maintenance, and operation, you can ensure optimal performance and maximize the benefits of your induction hot air heater.
As technology continues to advance,is poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of efficient and sustainable heating solutions. Embracing the advantages of induction hot air heaters can help businesses and homeowners alike achieve their heating goals while reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.