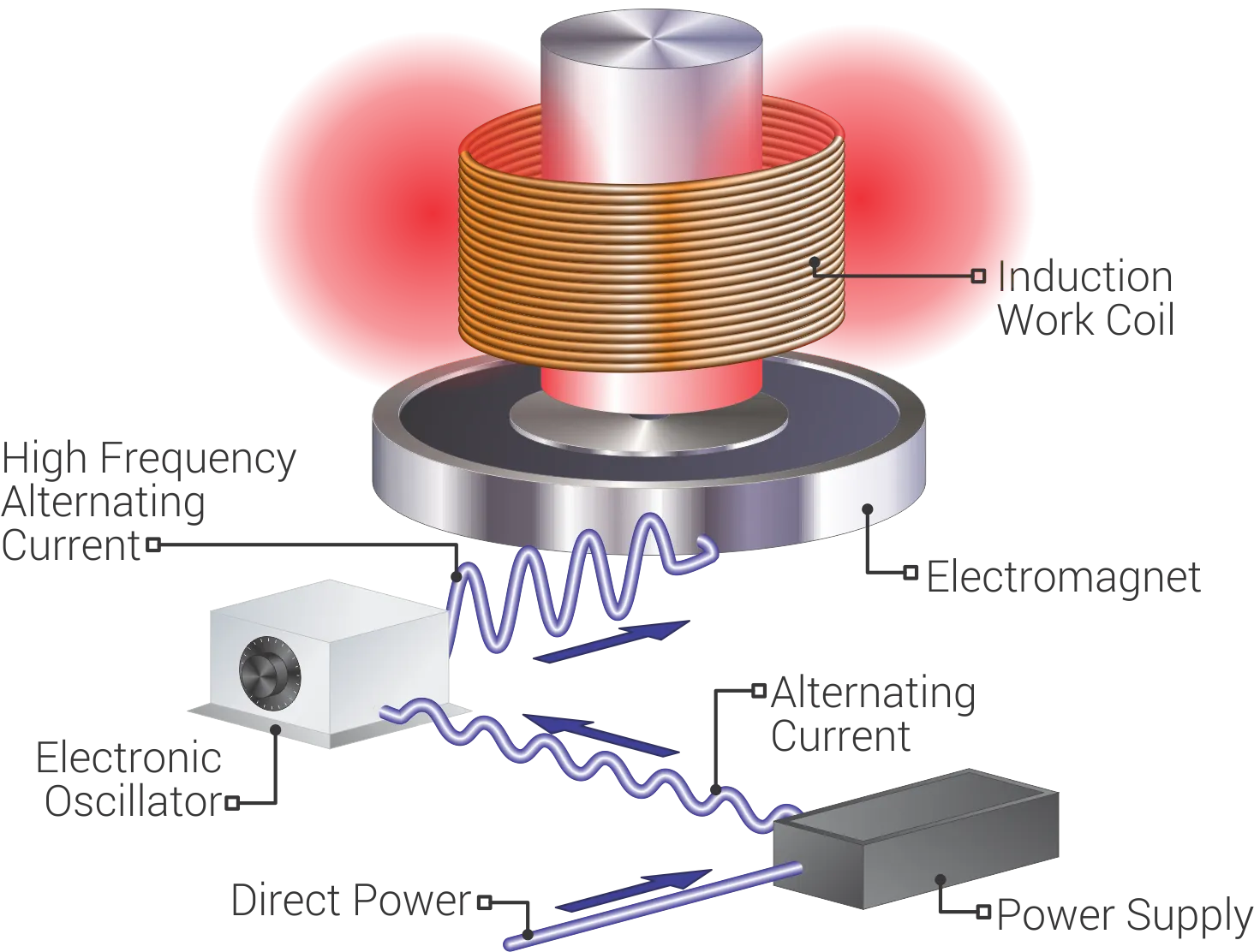
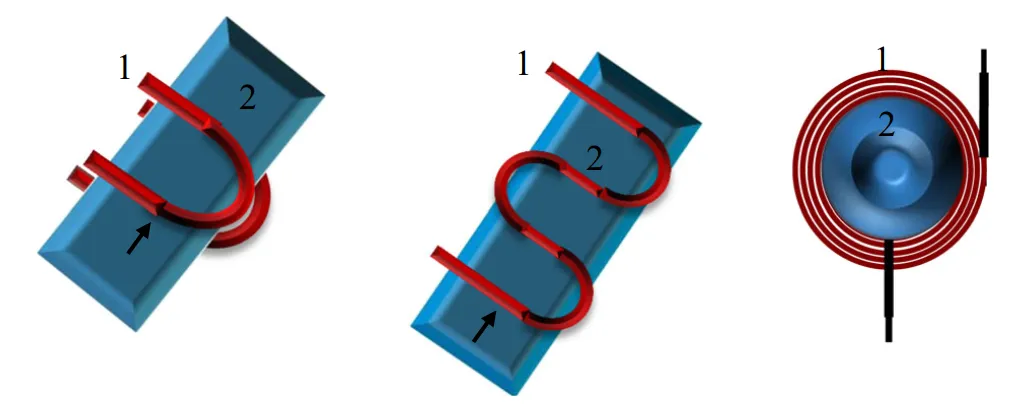
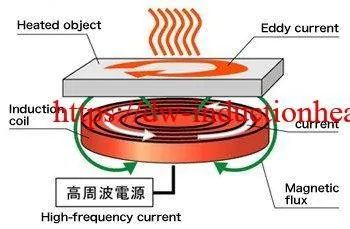
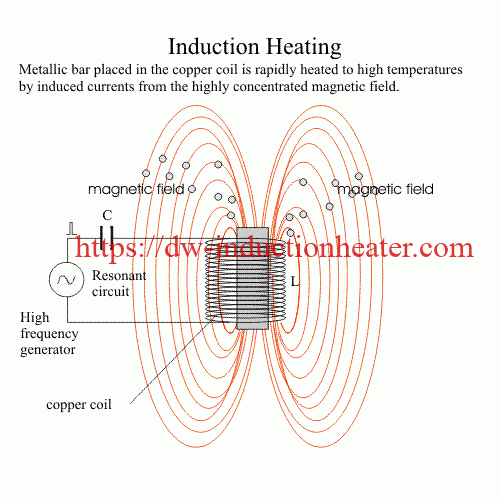
A source of high frequency electricity is used to drive a large alternating current through a induction coil. This induction heating coil is known as the work coil. See the picture opposite.
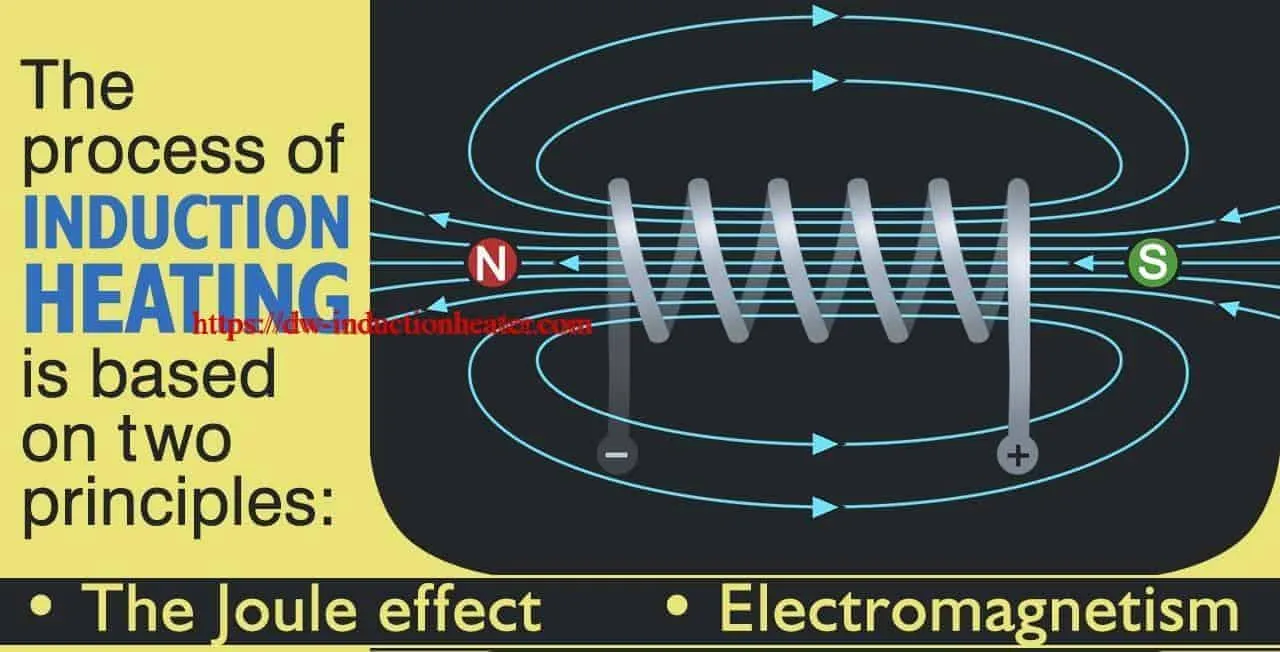
The passage of current through this induction heating coil generates a very intense and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the work coil. The workpiece to be heated is placed within this intense alternating magnetic field.
Depending on the nature of the workpiece material, a number of things happen…
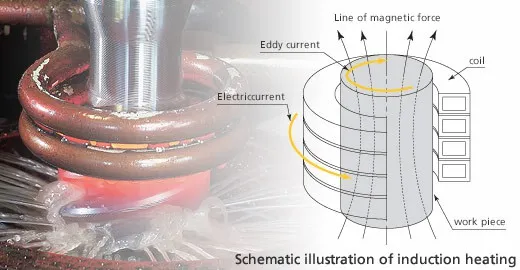
The alternating magnetic field induces a current flow in the conductive workpiece. The arrangement of the work coil and the workpiece can be thought of as an electrical transformer. The work coil is like the primary where electrical energy is fed in, and the workpiece is like a single turn secondary that is short-circuited. This causes tremendous currents to flow through the workpiece. These are known as eddy currents.
In addition to this, the high frequency used in Induction Heating applications gives rise to a phenomenon called skin effect. This skin effect forces the alternating current to flow in a thin layer towards the surface of the workpiece. The skin effect increases the effective resistance of the metal to the passage of the large current. Therefore it greatly increases the induction heating effect of the induction heater caused by the current induced in the workpiece.
[pdf-embedder url=”https://dw-inductionheater.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/induction_heating_principle-1.pdf” title=”induction_heating_principle”]