- 1/5
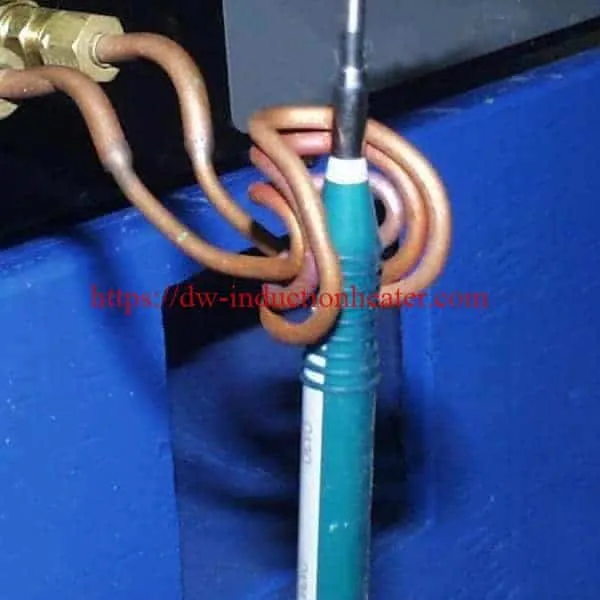

- 2/5
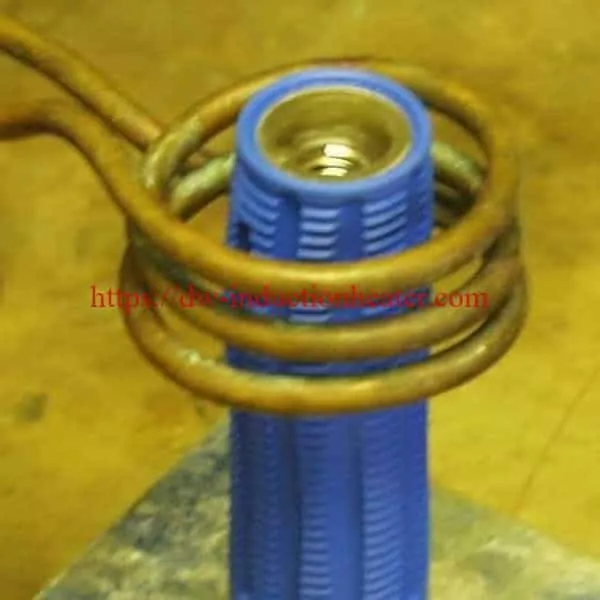

- 3/5
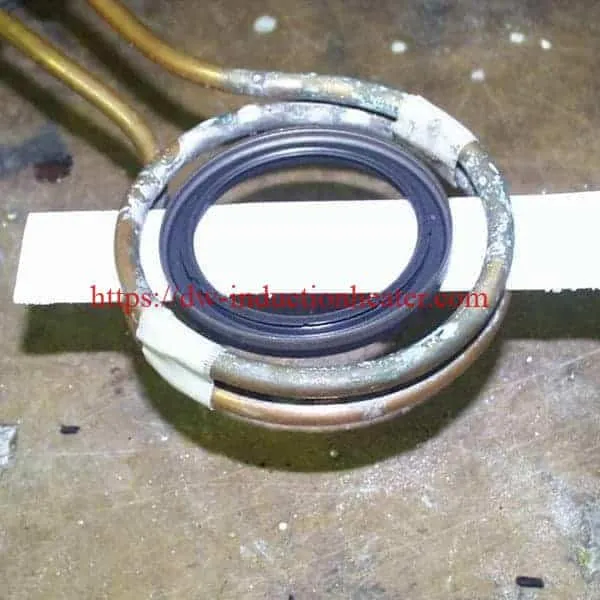

- 4/5

Induction Bonding
Description
What is induction bonding?
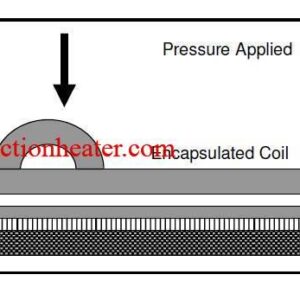
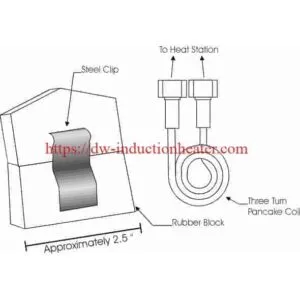
Induction bonding uses induction heating to cure bonding adhesives. Induction is the main method for curing adhesives and sealants for car components such as doors, hoods, fenders, rearview mirrors and magnets. Induction also cures the adhesives in composite- to-metal and carbon fiber-to-carbon fiber joints. There are two main types of automotive bonding: spotbonding, which heats small segments of the materials to be joined; full-ring bonding, which heats complete joints.

What are the benefits?
DAWEI Induction bonding systems ensure precise energy inputs for each panel. Small heat affected zones minimize total panel elongation. Clamping is not needed when bonding steel panels, which reduces stresses and distortion. Each panel is electronically monitored to ensure that energy input deviations are within tolerances. With full-ring bonding, a one-sizefits- all coil reduces the need for spare coils.
Where is it used?
Induction Heating is the preferred bonding method in the automotive industry. Widely used to bond steel and aluminum sheet metal, induction is increasingly employed to bond new lightweight composite and carbon fiber materials. Induction is used to bond curved strands, brake shoes and magnets in the electrotechnical industry. It is also used for guides, rails, shelves and panels in the white goods sector.
What equipment is available?
The DW-UHF and DW-HF series are the primary induction heating power supplies for induction bonding applications.