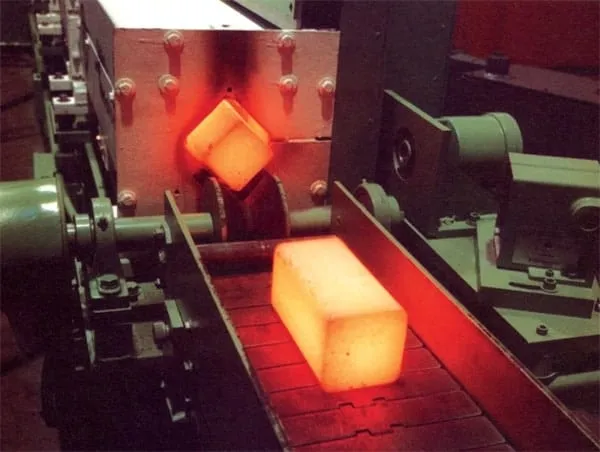
Induction Hot forming and Forging Process
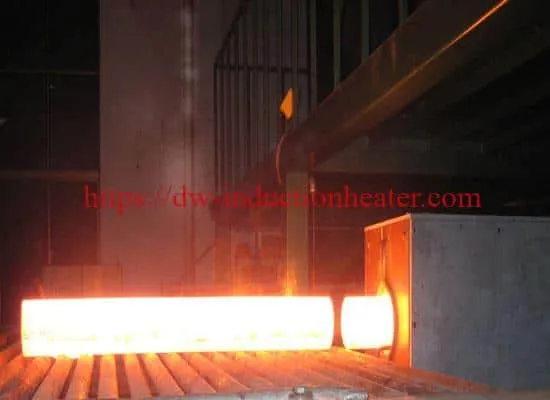
Induction Hot forming is a process in the manufacture of industrial fasteners such as bolts, screws and rivets. Heat is used to soften the metal which is usually a sheet, bar, tube or wire and then pressure is used to alter the shape of the metal by performing any of the following operations: hot heading, blanking, punching, slotting, perforating, trimming, shearing or bending. Besides, billet heating is also a process best performed with induction hot forming.
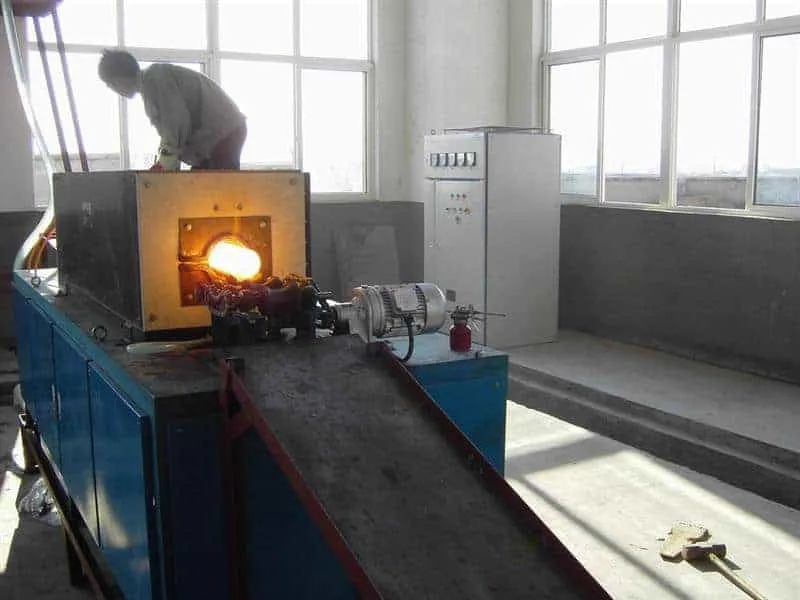
SAMSUNG DIGITAL CAMERAModern induction heating provides many advantages over other heating methods and is commonly used for bonding applications. Heating through induction provides reliable, repeatable, non-contact and energy-efficient heat in a minimal amount of time. Induction heating is also ideal for in-line production processes because of its ability to produce repeatable, rapid and accurate heating cycles.
Hot Forming and Forging, hot stamping and extrusion consist of forming a part that has been previously heated to a temperature at which its resistance to deformation is weak. The approximate hot forming temperatures of the most commonly used industrial materials are:
- Steel from 1100 to 1250 ºC
- Brass 750 ºC
- Aluminium 550ºC
After heating up the material, the hot forming operation is done on different types of machines: mechanical impact presses, bending machines, hydraulic extrusion presses, etc.
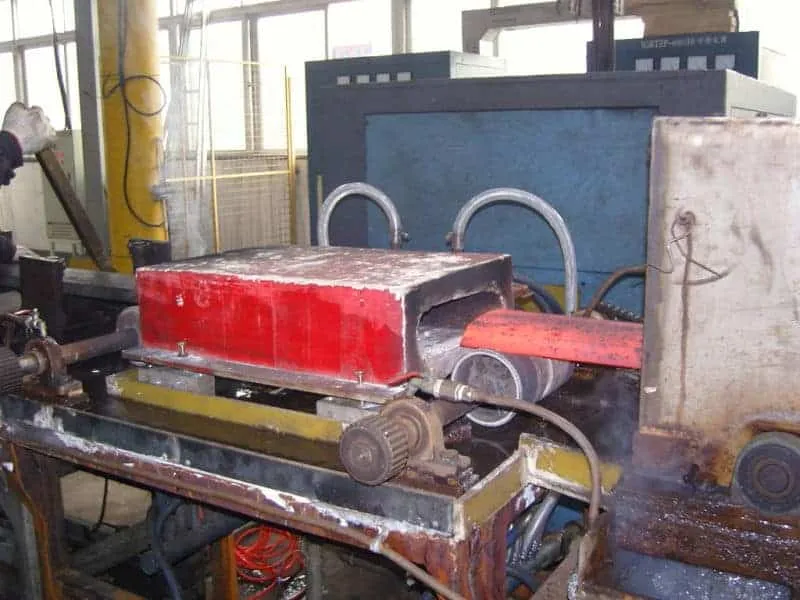
The starting material used in forging is presented in the form of rounded studs, squares (billet) or bar materials.
Conventional furnaces (gas, fuel) are used to heat the parts but also induction can be used.
Induction heating advantages:
- Material and energy saving plus flexibility
- Greater quality
- Process control
- Much shorter heating times
- Less oxidise and the production of scale is very low
- Easy and accurate adjustment of the temperature to be applied
- No time needed for the furnace pre and maintenance heating (for example after or during the weekend when it takes more time)
- Automation and reduction of the labour required
- Heat can be directed to one specific point, which is highly important for parts with only one forming area
- Greater thermal efficiency
- Better working conditions as the only heat present in the air is that of the parts themselves
The process of forging and hot forming is a common process in the manufacture of many industrial sectors such as automotive, railway, aerospace, oil and gas, chains and forging.