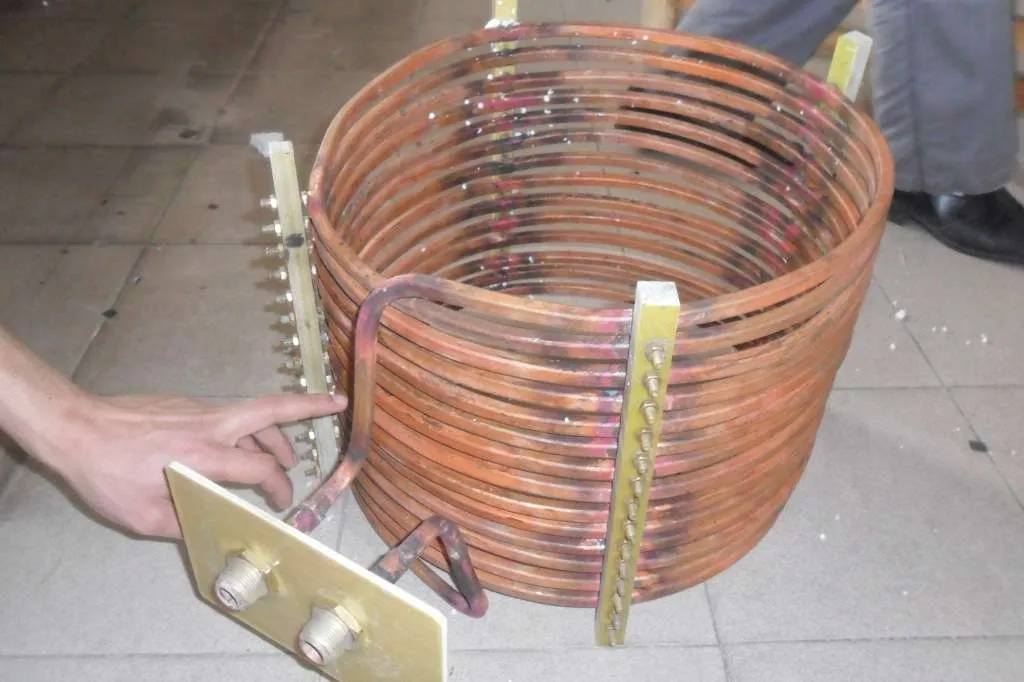
Induction heating coils are a type of heating element commonly used in induction heating systems. These coils are typically made of copper or other conductive materials and are designed to generate an alternating magnetic field when an alternating electrical current passes through them. The alternating magnetic field induces eddy currents in the object being heated, causing it to rapidly heat up. Induction heating coils are widely used in various industrial applications such as metalworking, heat treatment, and soldering, as they offer fast and efficient heating with precise temperature control.
In today’s fast-paced world, industries are constantly seeking innovative and efficient ways to improve their manufacturing processes. One such technological advancement that has revolutionized heat treatment technologies is the induction heating coil. Induction heating coils are widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and manufacturing, due to their ability to generate heat quickly and precisely. This article aims to explore the working principles, applications, advantages, and future prospects of induction heating coils.
1. Working Principles of Induction Heating Coils
Induction heating coils operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The process involves passing an alternating current (AC) through a coil, which generates a magnetic field. When a conductive material is placed within this magnetic field, eddy currents are induced in the material. These eddy currents generate heat due to the resistance of the material. The heat generated can be controlled by adjusting the frequency and power of the alternating current.
2. Types of Induction Heating Coils
There are several types of induction heating coils available, each designed for specific applications. Some common types include:
2.1. Helical Heating Coils
Helical coils consist of a single wire wound in a helix shape. They are suitable for heating cylindrical objects, such as pipes or rods, as the helical shape allows for uniform heating along the length of the object.
2.2. Pancake Coils
Pancake coils, also known as flat coils, are flat, circular coils that are ideal for heating flat or irregularly shaped objects. They provide a concentrated magnetic field, ensuring efficient and localized heating.
2.3. Cylindrical Coils
Cylindrical coils are designed for heating large, cylindrical objects, such as barrels or tanks. They are typically made up of multiple turns of wire wound around a cylinder, providing a uniform magnetic field for even heating.
2.4. Induction Coils for Hardening
Induction coils for hardening are specialized coils used in the heat treatment process known as induction hardening. These coils are designed to achieve rapid and precise heating of specific areas of a metal component, resulting in increased hardness and wear resistance.
2.5 Fork Coils
Fork coils have two fork-like tines that are used to heat two opposing sides of a workpiece. They are often used for brazing applications.
 3. Applications of Induction Heating Coils
3. Applications of Induction Heating Coils
3.1. Surface Hardening
One of the primary applications of induction heating coils is surface hardening. The localized heating provided by these coils allows for precise control over the hardening process, resulting in improved wear resistance and durability of components such as gears, shafts, and bearings.
3.2. Brazing and Soldering
Induction heating coils are widely used in brazing and soldering applications. The rapid and localized heating provided by these coils enables efficient joining of various metal components, including pipes, wires, and electronic components.
3.3. Annealing and Stress Relieving
Induction heating coils are also used for annealing and stress relieving processes. These processes involve heating metal components to a specific temperature and then gradually cooling them. Induction heating coils provide precise and controlled heating, ensuring uniformity throughout the component.
3.4. Shrink Fitting
Shrink fitting is a process that involves heating a metal component to expand it, allowing for easy assembly with another component. Induction heating coils provide rapid and localized heating, making them ideal for shrink fitting applications in industries such as automotive and manufacturing.
3.5. Melting and Casting
Induction heating coils are commonly used for melting and casting metals. The high-frequency heating provided by these coils allows for efficient and controlled melting of various metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper.
4. Advantages of Induction Heating Coils
4.1. Efficiency and Energy Savings
Induction heating coils offer high energy efficiency due to their ability to generate heat directly within the material being heated. This eliminates the need for preheating and minimizes heat losses, resulting in significant energy savings.
4.2. Rapid Heating
Induction heating coils provide rapid heating, allowing for shorter process times and increased productivity. This is especially beneficial in industries where time is a critical factor, such as automotive and electronics manufacturing.
4.3. Precise and Controlled Heating
Induction heating coils offer precise and controlled heating, enabling manufacturers to achieve consistent and uniform results. The ability to adjust the power and frequency of the alternating current allows for precise temperature control, ensuring the desired heat treatment outcome.
4.4. Safety and Environmentally Friendly
Induction heating coils are a safe and environmentally friendly heating solution. As heat is generated directly within the material being heated, there is no open flame or hot surface, minimizing the risk of accidents. Additionally, induction heating coils do not produce harmful emissions or waste, making them a sustainable choice.
5. Future Prospects and Innovations
The field of induction heating coils continues to evolve, with ongoing research and development focused on enhancing their performance and expanding their applications. Some future prospects and innovations include:
5.1. Integration with Industry 4.0 Technologies
The integration of induction heating coils with Industry 4.0 technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), holds great potential. This integration can enable real-time monitoring and control of the heating process, optimizing efficiency and productivity.
5.2. Advancements in Coil Design
Advancements in coil design, such as the use of advanced materials and geometries, can further enhance the efficiency and performance of induction heating coils. These advancements can lead to improved heat distribution, reduced energy consumption, and increased durability.
5.3. Development of New Heating Techniques
Researchers are continuously exploring new heating techniques using induction heating coils. Techniques such as selective heating, where specific areas of a component are heated, and simultaneous heating of multiple components are being studied for their potential applications in various industries.
Conclusion
Induction heating coils have revolutionized heat treatment technologies, offering efficient, precise, and controlled heating solutions. Their applications in surface hardening, brazing, annealing, and many other processes have significantly improved manufacturing processes across various industries. With ongoing advancements and innovations, the future of induction heating coils looks promising, with potential integration with Industry 4.0 technologies and the development of new heating techniques. As industries continue to strive for improved productivity and sustainability, induction heating coils will undoubtedly play a crucial role in meeting these goals.


