-
1/4

-
2/4

-
3/4
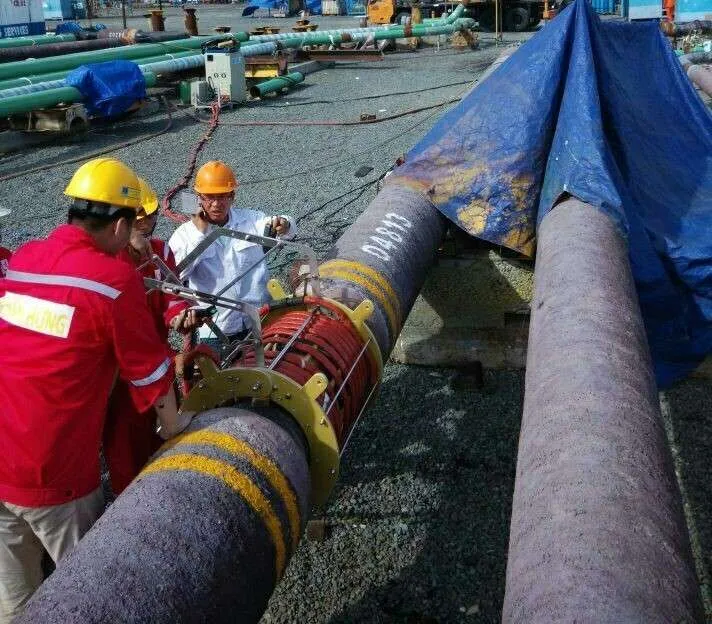

Induction Curing: The Future of Manufacturing
Induction Curing: The Future of Manufacturing
Induction curing is a new technology that is changing the future of manufacturing.  It is an eco-friendly and cost-effective way to cure coatings, adhesives, and other materials. Induction curing uses electromagnetic induction to produce heat within materials, which allows for faster curing times and a more efficient use of energy.The process is clean, precise, and reliable, with consistent results every time. It is also highly customizable, making it ideal for a variety of applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
It is an eco-friendly and cost-effective way to cure coatings, adhesives, and other materials. Induction curing uses electromagnetic induction to produce heat within materials, which allows for faster curing times and a more efficient use of energy.The process is clean, precise, and reliable, with consistent results every time. It is also highly customizable, making it ideal for a variety of applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Induction Curing: A Revolutionary Technology for Fast and Efficient Curing
Induction curing is a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat and cure materials such as adhesives, coatings, and composites. Unlike traditional curing methods that rely on heat transfer through convection or radiation, induction curing heats the material directly through induced electric currents.
This technology has gained popularity in recent years due to its numerous advantages over conventional curing methods. Here are some of the benefits of induction curing:
1. Faster curing times: Induction curing can cure materials much faster than conventional methods. This is because the heat is generated directly within the material, resulting in a more rapid and efficient curing process.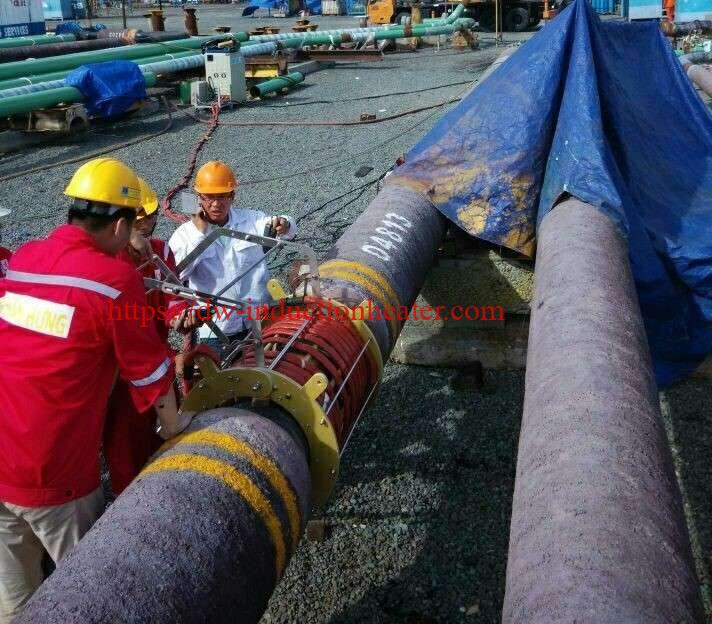
2. Reduced energy consumption: Induction curing requires less energy than traditional curing methods, making it more environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
3. Precise control: Induction curing allows for precise temperature control, ensuring that the material is cured evenly and consistently.
4. Improved quality: Induction curing can improve the quality of the cured material by minimizing the risk of overheating, reducing the potential for defects, and improving bonding strength.
5. Versatile applications: Induction curing can be used for a wide range of materials such as adhesives, coatings, and composites, making it a versatile technology that can be applied across multiple industries.
1. What is Induction Curing and How Does it Work?
Induction curing is a relatively new technology in the field of manufacturing. It is a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat and cure various materials. Induction curing is a highly efficient and cost-effective method that is gradually replacing traditional curing methods like baking. The process of induction curing works by passing electromagnetic energy through a coil, which creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field generates heat in the material that needs to be cured. The heat generated causes the material to cure and harden, creating a strong bond. The induction curing process is incredibly precise, and it can be used to cure a wide variety of materials, including composites, plastics, and adhesives. The process is also highly efficient, as it uses only the energy required to cure the material, reducing waste and energy usage. Induction curing is quickly becoming the future of manufacturing, as it offers a range of benefits when compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
2. Benefits of Induction Curing
Induction curing is the latest innovation in the manufacturing industry. It is quickly becoming the new standard for curing and drying materials. There are several benefits of induction curing that are quickly making it the preferred choice over traditional methods. First, induction curing is extremely efficient. It is capable of curing materials much faster than traditional methods due to the intense heat that is generated by the electromagnetic field. This means that production can be increased, and costs can be reduced. Second, induction curing is very precise. It provides a consistent and uniform heating across the entire surface of the material, eliminating hot spots and ensuring that the material is cured evenly. Third, induction curing is very energy-efficient. Unlike traditional curing methods that require a lot of energy to heat up large ovens or drying rooms, induction curing uses only the energy required to heat the material. Finally, induction curing is very safe. There is no open flame or hot surfaces, making it much safer for workers and the environment. With all of these benefits, it is easy to see why induction curing is quickly becoming the future of manufacturing.
3. Applications of Induction Curing in Manufacturing
Induction curing is a revolutionary technology that is at the forefront of manufacturing. It has a wide range of applications that make it an ideal choice for various manufacturing processes. One of the most significant advantages of induction curing is its ability to provide controlled, fast, and safe heating. This makes it ideal for curing adhesives, coatings, and other materials that require a specific temperature to cure. Induction curing is also ideal for manufacturing processes where high precision is required. This technology can provide highly accurate temperature control that ensures consistency in the manufacturing process. This makes it ideal for manufacturing processes such as semiconductor fabrication, medical device manufacturing, and other high-precision manufacturing applications. Another significant advantage of induction curing is its scalability. This technology can be scaled up or down to suit the specific needs of the manufacturing process. This makes it ideal for small-scale manufacturing processes as well as large-scale manufacturing processes. Induction curing is also very energy-efficient, making it an ideal choice for manufacturers who are looking to reduce their energy consumption and carbon footprint. This technology can reduce energy consumption by up to 80% compared to conventional heating methods. Overall, induction curing has a wide range of applications in manufacturing. Its ability to provide controlled, fast, and safe heating, high precision, scalability, and energy efficiency makes it an ideal choice for various manufacturing processes.
4. The Future of Induction Curing in Manufacturing.
The future of induction curing in manufacturing is incredibly bright. As technology continues to advance, induction curing is becoming more efficient, more cost-effective, and more environmentally friendly. It is a clean and efficient process that is already being used in a variety of manufacturing applications, including automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. One of the most significant advantages of induction curing is that it reduces the need for ovens and other high-temperature heat sources. This not only saves energy but also reduces the risk of fire hazards in the manufacturing process. 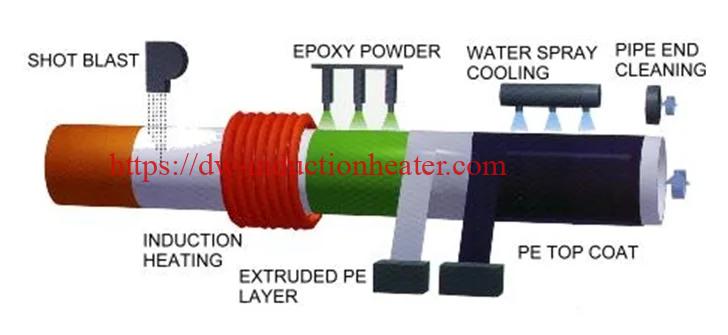 The process is also incredibly precise, allowing manufacturers to create parts with exact specifications and tolerances. In the coming years, we can expect to see continued advancements in induction curing, including the development of new materials and processes that will make it even more efficient and effective. As a result, we can expect to see increased adoption of induction curing in a variety of industries, including the automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing sectors. Overall, the future of induction curing is incredibly bright, and it is poised to become an essential part of the manufacturing landscape. As more and more manufacturers begin to realize the benefits of this innovative technology, we can expect to see increased efficiency, reduced costs, and more eco-friendly manufacturing processes across a range of industries.
The process is also incredibly precise, allowing manufacturers to create parts with exact specifications and tolerances. In the coming years, we can expect to see continued advancements in induction curing, including the development of new materials and processes that will make it even more efficient and effective. As a result, we can expect to see increased adoption of induction curing in a variety of industries, including the automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing sectors. Overall, the future of induction curing is incredibly bright, and it is poised to become an essential part of the manufacturing landscape. As more and more manufacturers begin to realize the benefits of this innovative technology, we can expect to see increased efficiency, reduced costs, and more eco-friendly manufacturing processes across a range of industries.
Induction curing is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where fast and efficient curing is crucial. For example, in the automotive industry, induction curing is used to bond components together, seal joints, and cure paint and coatings.
In conclusion, induction curing is a revolutionary technology that offers numerous benefits over traditional curing methods. It is faster, more energy-efficient, and provides precise temperature control, resulting in improved quality and greater versatility. As such, it is becoming increasingly popular across a wide range of industries, and its use is likely to continue to grow in the coming years.
