-
1/4

-
2/4

-
3/4

-
4/4

CNC Metals Seam Welders-Seam Welding Machines-Roller Seam Welding Machines
Seam Welding Machines: Everything You Need to Know
Metals Seam welding machines play a crucial role across various industries, providing reliable and efficient solutions for joining metal components. From automotive manufacturing to aerospace applications, these machines have revolutionized welding processes with precision and consistency. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of seam welding machines, their working principles, types, applications, benefits, and factors to consider while purchasing one. By the end of this article, you will have an in-depth understanding of seam welding machines and why they are essential in many industrial operations.
1. What Are Seam Welding Machines?
Seam welding machines are specialized equipment used to join metal parts along a continuous seam. They utilize a welding process that involves heat and pressure to fuse two or more pieces of material. These machines are commonly seen in operations where leak-tight or structurally strong seams are required, such as in the construction of pipes, tanks, and vehicle parts.
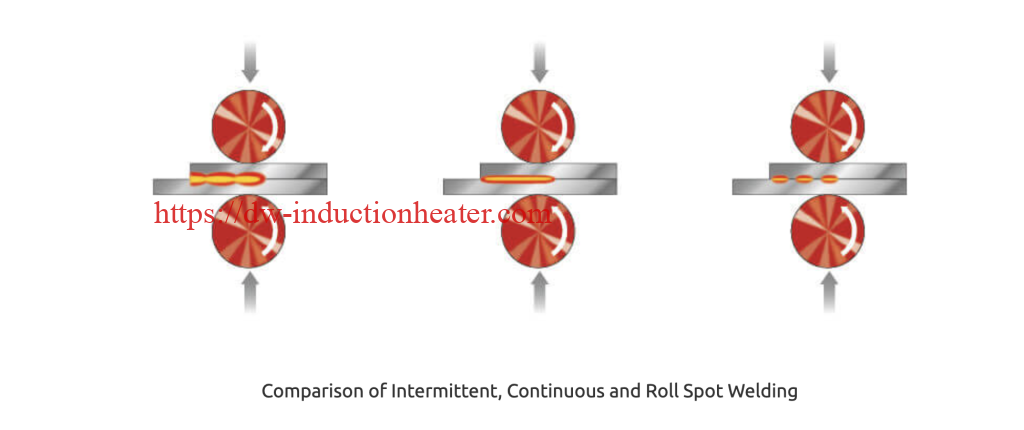
Instead of separate weld points as found in spot welding, seam welding produces a continuous, strong, and uniform weld along the length of the metal components being joined. This consistency makes seam welding machines indispensable for many industries seeking durability and aesthetic appeal in their products.
2. How Does a Seam Welding Machine Work?
The functioning of a seam welding machine is based on resistance welding principles. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Metal Components Placement
The materials to be welded are placed between two rotating copper electrodes, which apply consistent pressure throughout the welding process. - Electric Current Application
A high-level electric current passes through the electrodes, generating intense localized heat at the point of contact between the two materials. - Controlled Movement
The rotating electrodes steadily move along the seam, applying heat and pressure, which ensures a continuous weld. - Cooling Period
The electrodes cool rapidly as they move, solidifying the weld and minimizing the risk of deformation.
This process is both efficient and durable, producing welds that are reliable and free of imperfections.
3. Types of Seam Welding Machines
Seam welding machines come in a variety of configurations based on their intended applications, welding process, and other parameters. Here are some of the most common types:
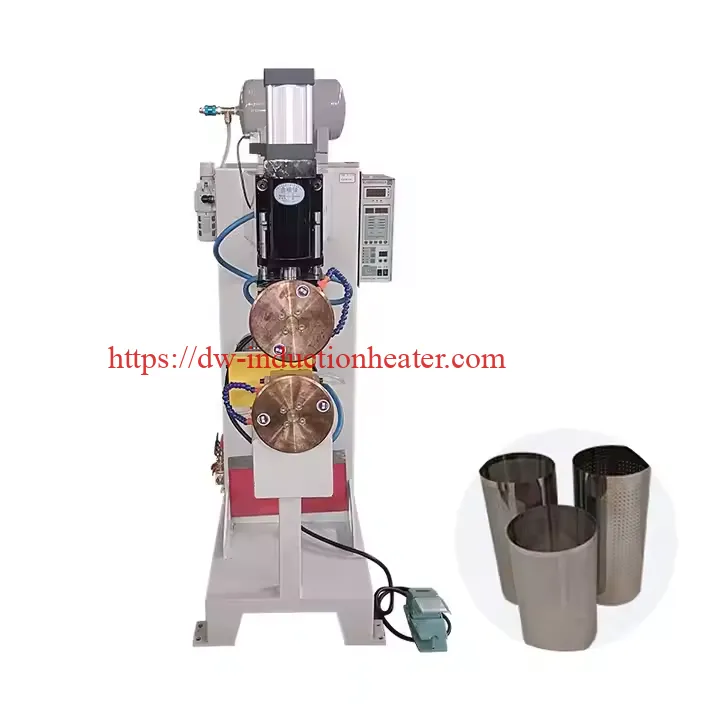
a. Roll Seam Welding Machines
These machines use circular electrodes to create overlapping welds that form a continuous seam. Roll seam welding is widely used in manufacturing liquid-tight containers like fuel tanks and radiators.
b. Longitudinal Seam Welding Machines
Longitudinal seam welding machines weld materials along their length, making them ideal for joining tubes, pipes, and cylindrical components.
c. Circular Seam Welding Machines
As the name suggests, these machines are designed to weld along circular seams. They are commonly used in the production of pressure vessels and flanges.
d. Resistance Seam Welding Machines
These machines rely solely on resistance welding principles, where current, time, and pressure are applied to join metals effectively.
e. Projection Seam Welding Machines
Projection welding machines use localized heat and pressure at predetermined points, creating weld lines instead of single points.
f. Automated Seam Welding Machines
Modern seam welding machinery comes with automated systems equipped with programmable features that enhance efficiency, precision, and repeatability.
4. Key Applications of Seam Welding Machines
Seam welding machines are used in a wide range of industries due to their versatility and reliability. Some of the most notable applications include:
- Automotive Manufacturing
Seam welding is essential in creating fuel tanks, exhaust systems, and car bodies. - Aerospace Industry
The precision of seam welding machines makes them suitable for constructing critical components like fuselage parts and fuel systems. - HVAC Systems
Seam welding machines are frequently used in the production of ducts, ventilation systems, and heat exchangers. - Food and Beverage Industry
These machines help in fabricating leak-proof food containers, cans, and bottles. - Oil and Gas Sector
Seam welding is vital for the creation of pipelines, pressure vessels, and storage tanks to ensure leak-tight construction. - Electronics Manufacturing
Seam welding machines are utilized for joining electrical enclosures and battery packs.
5. Benefits of Using Seam Welding Machines
Seam welding machines have become the go-to solution for industrial welding applications due to their numerous advantages. Below are the key benefits:
a. Consistent Weld Quality
The automated nature of seam welding machines ensures uniform welds with minimal variation, reducing the risk of weak spots or defects.
b. High Productivity
Seam welding is much faster than traditional welding techniques and allows continuous operation, significantly enhancing productivity.
c. Cost-Effectiveness
Although the initial setup can be expensive, these machines reduce labor costs and material wastage, leading to long-term savings.
d. Leak-Proof Welds
Seam welding is popular in industries where leak-proof joints are essential, such as in fuel tanks or food containers.
e. Strong and Durable Bonds
The process produces welds that are not only visually appealing but also structurally stable for high-performance applications.
f. Versatility
With advancements in technology, seam welding machines now cater to a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
6. Factors to Consider While Buying a Seam Welding Machine
When purchasing a seam welding machine, it’s essential to select the right one based on your operational requirements. Here are the crucial factors to consider:
a. Application Requirements
Identify the specific welding needs of your industry, such as material thickness, seam type, and production volume.
b. Machine Specifications
Evaluate critical machine parameters such as welding speed, electrode size, and power capacity to ensure compatibility with your desired output.
c. Automation Features
Opt for machines equipped with advanced automation and programmability, which can improve precision and save time during production.
d. Build Quality
Invest in machines made from high-quality, durable materials to ensure a longer lifespan and minimal maintenance.
e. Cost and Budget
Assess your budget and consider the machine’s initial cost versus the long-term benefits.
f. Support and Servicing
Choose a manufacturer that offers excellent customer support, training, and after-sales service for the machine.
7. Seam Welding vs. Spot Welding: Key Differences
Although seam welding and spot welding share similarities, they differ in their applications and results. Here are the major distinctions:
| Aspect | Seam Welding | Spot Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Type | Continuous weld | Discrete weld points |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Application | Used for pipes and containers | Used for sheet metal assemblies |
| Leak-Proof Joints | Yes | No |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced machinery | Lower |
8. Material Compatibility
Seam welding machines can work with a wide variety of materials, including:
- Stainless Steel – Common in the automotive and food industry.
- Aluminum – Preferred for lightweight applications in aerospace.
- Carbon Steel – Popular in construction and oil pipeline manufacturing.
- Brass and Copper – Used for specific electrical components.
It is important to ensure that the material’s properties match the machine’s capabilities to achieve optimal results.
9. Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Seam Welding Machines
Proper maintenance is the key to extending the lifespan of seam welding machines and ensuring uninterrupted performance. Here are a few tips:
Regular Inspection
Check the electrodes, rollers, and other essential components periodically for wear and tear.
Timely Cleaning
Remove debris, oxidation, and other contaminants from machine parts to maintain efficiency.
Calibration
Ensure the machine is calibrated according to the project requirements.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Uneven Welds: Check the alignment of electrodes.
- Overheating: Optimize the current or cooling system.
- Surface Cracking: Inspect materials for cleanliness or reduce welding speed.
10. The Future of Seam Welding Technology
With the advancements in robotics and AI, the future of seam welding machines looks promising. Automated seam welding with enhanced precision and reduced human intervention is already becoming a reality. Additionally, the integration of IoT technology allows for real-time monitoring and data analysis, making machines smarter and more efficient.
Sustainability is also driving new innovations, with manufacturers developing eco-friendly seam welding solutions that consume less energy and reduce carbon footprints.
11.Technical Specifications of Seam Welding Machines
Below is a detailed technical table that outlines the performance and operational parameters of seam welding machines. The specifications can vary depending on the specific machine model and its intended application.
| Specification | Details |
| Welding Method | Resistance Seam Welding (RSEW) |
| Power Supply | Single-phase or three-phase (220V, 380V, or custom) |
| Rated Welding Current | 2,000 A – 50,000 A |
| Electrode Wheel Diameter | 50 mm – 400 mm |
| Electrode Material | Copper alloys (RWMA Class 1/2) |
| Welding Speed | 0.5 – 20 m/min |
| Material Thickness Capacity | 0.1 mm – 10 mm |
| Cooling System | Water-cooled electrodes and transformer |
| Control Type | Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or Advanced Microcomputer |
| Maximum Welding Pressure | Up to 10,000 N |
| Electrode Force Control | Pneumatic or servo-controlled systems |
| Seam Spacing Options | Adjustable (as per material or process) |
| Duty Cycle | Up to 50% (depending on configuration) |
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Seam welding machines are an integral part of modern manufacturing, delivering efficiency, durability, and precision across numerous industries. From automotive production to aerospace engineering, their applications are diverse and essential. By understanding the types, applications, benefits, and maintenance of these machines, businesses can make informed decisions when investing in them.
Selecting the right seam welding machine based on your operational needs and ensuring proper maintenance will guarantee long-term success. As technology evolves, seam welding machines will continue to transform industries, setting new benchmarks for quality and productivity.
If you’re seeking a reliable welding solution for your business, seam welding machines are a game-changer that can optimize your production processes and deliver exceptional results.